Mebiol Gel
Mebiol
- Catalog No.:
- MBG-PMW20-1001
- Shipping:
- Calculated at Checkout
Note:
This product is packaged with RP Drying Agent packs to absorb moisture, oxygen and corrosive gases. It is therefore subject to European Commerce Area Import Regulation (EC) No. 1272/2008 - Classification, Labeling, and Packaging of Substances and Mixtures (CLP). Applies to EEA (i.e. EU27 countries, Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway, UK).
For additional information, see the following:
OSHA Europe
RP Agent Manufactuer's Statement
Introduction to Mebiol® Gel
Hydrogels are a diverse class of polymeric materials characterized by their network-like structure and high water content. Hydrogels of many kinds have found a wide variety of applications in medicine and life science research weighted towards, but not at all limited to three-dimensional cell culture, tissue engineering, and drug delivery. Properties highly favorable to cell culture and tissue engineering applications prompted the commercialization of Mebiol® Gel, a copolymer of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) and poly(ethylene glycol) (PNIPAAm-PEG) for research purposes in the early 2000's.
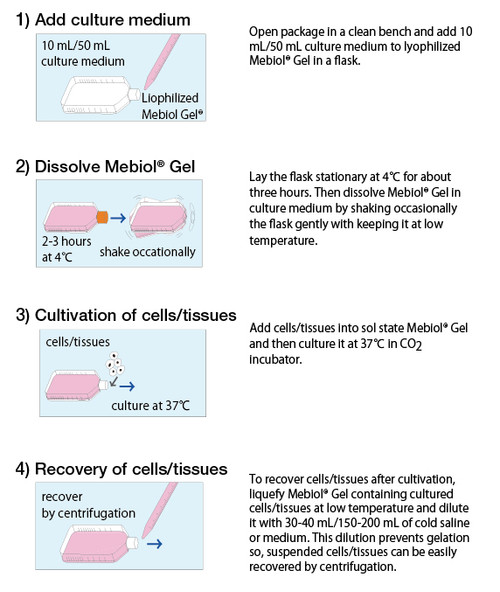
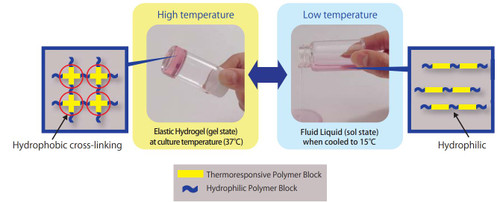
Mebiol® Gel's defining feature, in contrast to other commercially available hydrogels, is its temperature reversible sol-gel transition. When cooled, Mebiol® Gel is a sol (handles like a liquid) but becomes a rigid hydrogel at higher temperatures. In practice, this means extremely easy cell handling. Cultures are seeded into cooled Mebiol® Gel and recovered conveniently by cooling the culture vessel and centrifugation. In the gel state, the highly lipophylic environment of the Mebiol® Gel presents an efficient niche for cell proliferation, cell communication, gas and mass exchange, and protection of cells and tissue from shear forces.
Low Temperature (Sol) High Temperature (Gel)
Features
- Easy handling
- Non-toxic, biocompatible
- 100% synthetic, pathogen free
- High transparency for cell observation
- Proven performance.
Preparation
Application
- Stem cell and pluripotent stem cell culture, expansion, and differentiation
- Spheroid culture
- Cell implantation
- Organ and Tissue Regeneration
- Drug Delivery
- Non-cell culture application
Application Examples
| 1) Culture of primary cancer cells in Mebiol Gel |
 Selective growth of only primary cancer cells from human cancerous tissue in Mebiol Gel (courtesy Dr. S. Kubota, Dept. of General Surgery, St. Marianna University School of Medicine). This technology enables the characterization of patient-derived primary cancer cells and therefore enabling the evaluation of primary cells for chemosensitivity, malignancy, metastasis activity and other parameters that might influence patient therapy. |
|
|
| 2) Stem Cell Culture |
  3D culture of undifferentiated mouse and Macaca ES cells cultured without LIF or feeder layer cells performed in collaboration with with Dr. K. Hishikawa, Dept. of Clinical Renal Regeneration, University of Tokyo. Left: 2D on Feeder Cells |
  The strong positive alkaline phosphatase staining of Macaca (primate) ES cells cultured in Mebiol® Gel suggests undifferentiation. Left: 2D on Feeder Cells |
| 3) Selective separate culture of somatic stem cell (mouse embryo skin origin) |
| Isolation of Epithelial Stem Cells from Dermis by a Three-dimensional Culture System Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 98 (1), 174-184 (2006) PMID: 16408300 |
| 4) Cartilage tissue reproduction by in vitro 3D culture of cartilage cell |
| Chondrocytes Containing Growth Factors in a Novel Thermoreversible Gelation Polymer Scaffold Tissue Engineering, 12 (5), 1237-1245 (2006) |
| 5) Bone induction by in vitro 3D culture of human mesenchymal cell stem cell (hMSC) |
| Gene expression profile of human mesenchymal stem cells during osteogenesis in three-dimensional thermoreversible gelation polymer Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 317, 1103-1107 (2004). PMID: 15094382 |
| 6) Production of hepatitis C viruses (HCV) by 3-D culture of human hepatocyte cell line |
| Production of infectious hepatitis C virus particles in three-dimensional cultures of the cell line carrying the genome-length dicistronic viral RNA of genotype 1b Virology, 351 (2), 381-392 (2006) PMID: 16678876 |
| 7) Passage control by local heating (on chip cell sorter system) |
| On-Chip Cell Sorting System Using Laser-Induced Heating of a Thermoreversible Gelation Polymer to Control Flow, Y. Shirasaki, J. Tanaka, H. Makazu, K. Tashiro, S. Shoji, S. Tsukita, T. Funatsu, Anal. Chem., 78, 695-701 (2006) PMID: 16448041 more |
Dynamic Viscoelastic Property of Mebiol® Gel
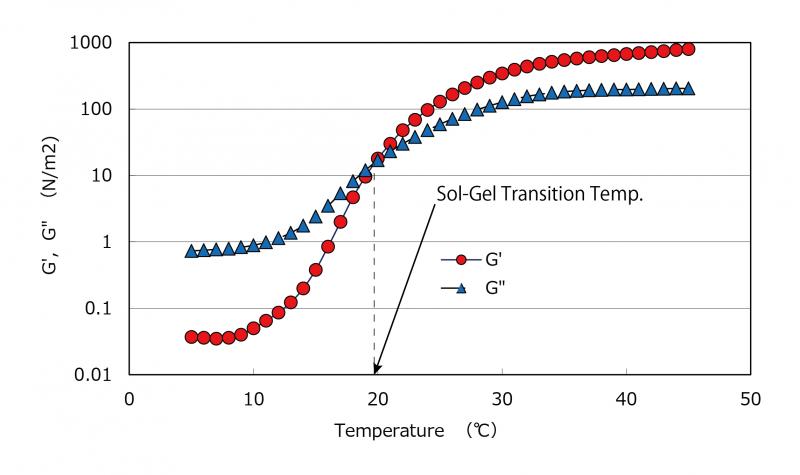
Temperature dependence of the dynamic moduli of the aqueous solution of Mebiol® Gel at a concentration of 10 wt% in distilled water. Storage modulus (G', solid lines) and loss modulus (G'', broken lines) were measured on heating (closed symbols) and cooling (open symbols) at the oscillatory frequency of 1 Hz.
| Documents & Links for Mebiol Gel | |
| Flyer | Mebiol® Gel Flyer |
| Datasheet | Mebiol Gel Datasheet |
| Documents & Links for Mebiol Gel | |
| Flyer | Mebiol® Gel Flyer |
| Datasheet | Mebiol Gel Datasheet |
| Citations for Mebiol Gel – 44 Found |
| Li, Qiang; Lin, Haishuang; Wang, Ou; Qiu, Xuefeng; Kidambi, Srivatsan; Deleyrolle, Loic P; Reynolds, Brent A; Lei, Yuguo. Scalable Production of Glioblastoma Tumor-initiating Cells in 3 Dimension Thermoreversible Hydrogels. Scientific Reports. 2016;6( 27549983):31915. PubMed |
| Tahir, Suhail; Fukushima, Yuji; Sakamoto, Keiko; Sato, Kyosuke; Fujita, Harumi; Inoue, Joe; Uede, Toshimitsu; Hamazaki, Yoko; Hattori, Masakazu; Minato, Nagahiro. A CD153+CD4+ T follicular cell population with cell-senescence features plays a crucial role in lupus pathogenesis via osteopontin production. Journal Of Immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950). 2015;194(12):5725-35. PubMed |
| Lei, Yuguo; Schaffer, David V. A fully defined and scalable 3D culture system for human pluripotent stem cell expansion and differentiation. Proceedings Of The National Academy Of Sciences Of The United States Of America. 2013;110(52):E5039-48. PubMed |
| Hiramatsu, Ryuji; Harikae, Kyoko; Tsunekawa, Naoki; Kurohmaru, Masamichi; Matsuo, Isao; Kanai, Yoshiakira. FGF signaling directs a center-to-pole expansion of tubulogenesis in mouse testis differentiation. Development (Cambridge, England). 2010;137(2):303-12. PubMed |
| Arai, Takao; Benny, Ofra; Joki, Tatsuhiro; Menon, Lata G; Machluf, Marcelle; Abe, Toshiaki; Carroll, Rona S; Black, Peter M. Novel local drug delivery system using thermoreversible gel in combination with polymeric microspheres or liposomes. Anticancer Research. 2010;30(4):1057-64. PubMed |
| Yamamoto, Masamichi; Beppu, Hideyuki; Takaoka, Katsuyoshi; Meno, Chikara; Li, En; Miyazono, Kohei; Hamada, Hiroshi. Antagonism between Smad1 and Smad2 signaling determines the site of distal visceral endoderm formation in the mouse embryo. The Journal Of Cell Biology. 2009;184(2):323-34. PubMed |
| Kimura-Yoshida, Chiharu; Nakano, Hiroshi; Okamura, Daiji; Nakao, Kazuki; Yonemura, Shigenobu; Belo, Jose A; Aizawa, Shinichi; Matsui, Yasuhisa; Matsuo, Isao. Canonical Wnt signaling and its antagonist regulate anterior-posterior axis polarization by guiding cell migration in mouse visceral endoderm. Developmental Cell. 2005;9(5):639-50. PubMed |
| Brown, Jacquelyn A; Faley, Shannon L; Judge, Monika; Ward, Patricia; Ihrie, Rebecca A; Carson, Robert; Armstrong, Laura; Sahin, Mustafa; Wikswo, John P; Ess, Kevin C; Neely, M Diana. Rescue of Impaired Blood-Brain Barrier in Tuberous Sclerosis Complex Patient Derived Neurovascular Unit. Biorxiv : The Preprint Server For Biology. 2023; 38168450( 38168450) PubMed |
| Dzurov, Matej; Pospíšilová, Šárka; Krafčíková, Michaela; Trantírek, Lukáš; Vojtová, Lucy; Ryneš, Jan. A thermosensitive gel matrix for bioreactor-assisted in-cell NMR of nucleic acids and proteins. Journal Of Biomolecular Nmr. 2023;77(5-6):203-215. PubMed |
| Miron, Alina; Ní Dhubhghaill, Sorcha; Kocaba, Viridiana; Jager, Martine J; Melles, Gerrit R J; Oellerich, Silke. Early and late-onset cell migration from peripheral corneal endothelium. Plos One. 18(5):e0285609. PubMed |
| Dzurov, Matej; Pospíšilová, Šárka; Krafčíková, Michaela; Trantírek, Lukáš; Vojtová, Lucy; Ryneš, Jan. A thermosensitive gel matrix for bioreactor-assisted in-cell NMR of nucleic acids and proteins. Journal Of Biomolecular Nmr. 2023;77(5-6):203-215. PubMed |
| Buzzaccaro, Stefano; Ruzzi, Vincenzo; Faleo, Tommaso; Piazza, Roberto. Microrheology of a thermosensitive gelling polymer for cell culture. The Journal Of Chemical Physics. 2022;157(17):174901. PubMed |
| Parfenov, Vladislav A; Khesuani, Yusef D; Petrov, Stanislav V; Karalkin, Pavel A; Koudan, Elizaveta V; Nezhurina, Elizaveta K; Pereira, Frederico DAS; Krokhmal, Alisa A; Gryadunova, Anna A; Bulanova, Elena A; Vakhrushev, Igor V; Babichenko, Igor I; Kasyanov, Vladimir; Petrov, Oleg F; Vasiliev, Mikhail M; Brakke, Kenn; Belousov, Sergei I; Grigoriev, Timofei E; Osidak, Egor O; Rossiyskaya, Ekaterina I; Buravkova, Ludmila B; Kononenko, Oleg D; Demirci, Utkan; Mironov, Vladimir A. Magnetic levitational bioassembly of 3D tissue construct in space. Science Advances. 2020;6(29):eaba4174. PubMed |
| Schröder, Agnes; Schöniger, Ricarda; Oeldemann, Juliane; Spanier, Gerrit; Proff, Peter; Jantsch, Jonathan; Kirschneck, Christian; Ullrich, Niklas. An Evaluation of Different 3D Cultivation Models on Expression Profiles of Human Periodontal Ligament Fibroblasts with Compressive Strain. International Journal Of Molecular Sciences. 2022;23(4) PubMed |
| Goggi, Julian L; Qiu, Lifeng; Liao, Mei Chih; Khanapur, Shivashankar; Jiang, Lingfan; Boominathan, Ramasamy; Hartimath, Siddesh V; Cheng, Peter; Yong, Fui Fong; Soh, Vanessa; Deng, Xiaozhou; Lin, Youshan Melissa; Haslop, Anna; Tan, Peng Wen; Zeng, Xiaoxia; Lee, Jolene W L; Zhang, Zhiwei; Sadasivam, Pragalath; Tan, Eng King; Luthra, Sajinder K; Shingleton, William D; Oh, Steve K W; Zeng, Li; Robins, Edward G. Dopamine transporter neuroimaging accurately assesses the maturation of dopamine neurons in a preclinical model of Parkinson's disease. Stem Cell Research & Therapy. 2020;11(1):347. PubMed |
| Li, Yi-Han; Chen, Tsung-Ming; Huang, Bu-Miin; Yang, Shang-Hsun; Wu, Chia-Ching; Lin, Yung-Ming; Chuang, Jih-Ing; Tsai, Shaw-Jenq; Sun, H Sunny. FGF9 is a downstream target of SRY and sufficient to determine male sex fate in ex vivo XX gonad culture. Biology Of Reproduction. 2020;103(6):1300-1313. PubMed |
| Chakrabarty, Sanjiban; Quiros-Solano, William F; Kuijten, Maayke M P; Haspels, Ben; Mallya, Sandeep; Lo, Calvin Shun Yu; Othman, Amr; Silvestri, Cinzia; van de Stolpe, Anja; Gaio, Nikolas; Odijk, Hanny; van de Ven, Marieke; de Ridder, Corrina M A; van Weerden, Wytske M; Jonkers, Jos; Dekker, Ronald; Taneja, Nitika; Kanaar, Roland; van Gent, Dik C. A Microfluidic Cancer-on-Chip Platform Predicts Drug Response Using Organotypic Tumor Slice Culture. Cancer Research. 2022;82(3):510-520. PubMed |
| Lin, Zuan-Tao; Gu, Jianhua; Wang, Huie; Wu, Albon; Sun, Jingying; Chen, Shuo; Li, Yaxi; Kong, Yifei; Wu, Mei X; Wu, Tianfu. Thermosensitive and Conductive Hybrid Polymer for Real-Time Monitoring of Spheroid Growth and Drug Responses. Acs Sensors. 2021;6(6):2147-2157. PubMed |
| Lei, Yuguo; Schaffer, David V. A fully defined and scalable 3D culture system for human pluripotent stem cell expansion and differentiation. Proceedings Of The National Academy Of Sciences Of The United States Of America. 2013;110(52):E5039-48. PubMed |
| Lei, Yuguo; Schaffer, David V. A fully defined and scalable 3D culture system for human pluripotent stem cell expansion and differentiation. Proceedings Of The National Academy Of Sciences Of The United States Of America. 2013;110(52):E5039-48. PubMed |
| Yook, Yeon Joo; Yoo, Kyung Hyun; Song, Seon Ah; Seo, Min Ji; Ko, Je Yeong; Kim, Bo Hye; Lee, Eun-Ji; Chang, Eunsun; Woo, Yu Mi; Park, Jong Hoon. Mxi1 influences cyst formation in three-dimensional cell culture. Bmb Reports. 2012;45(3):189-93. PubMed |
| Suzuki, Yoko; Ohno, Satoshi; Okuyama, Ryuji; Aruga, Atsushi; Yamamoto, Masakazu; Miura, Shigeki; Yoshioka, Hiroshi; Mori, Yuichi; Suzuki, Katsuhiko. Determination of chronic inflammatory states in cancer patients using assay of reactive oxygen species production by neutrophils. Anticancer Research. 2012;32(2):565-70. PubMed |
| Suzuki, Katsuhiko; Ohno, Satoshi; Suzuki, Yoko; Ohno, Yumiko; Okuyama, Ryuji; Aruga, Atsushi; Yamamoto, Masakazu; Ishihara, Ken-O; Nozaki, Tsutomu; Miura, Shigeki; Yoshioka, Hiroshi; Mori, Yuichi. Effect of green tea extract on reactive oxygen species produced by neutrophils from cancer patients. Anticancer Research. 2012;32(6):2369-75. PubMed |
| Suzuki, Katsuhiko; Ohno, Satoshi; Suzuki, Yoko; Ohno, Yumiko; Okuyama, Ryuji; Aruga, Atsushi; Yamamoto, Masakazu; Ishihara, Ken-O; Nozaki, Tsutomu; Miura, Shigeki; Yoshioka, Hiroshi; Mori, Yuichi. Effect of green tea extract on reactive oxygen species produced by neutrophils from cancer patients. Anticancer Research. 2012;32(6):2369-75. PubMed |
| Hiramatsu, Ryuji; Harikae, Kyoko; Tsunekawa, Naoki; Kurohmaru, Masamichi; Matsuo, Isao; Kanai, Yoshiakira. FGF signaling directs a center-to-pole expansion of tubulogenesis in mouse testis differentiation. Development (Cambridge, England). 2010;137(2):303-12. PubMed |
| Sitalakshmi, G; Sudha, B; Madhavan, H N; Vinay, S; Krishnakumar, S; Mori, Yuichi; Yoshioka, Hiroshi; Abraham, Samuel. Ex vivo cultivation of corneal limbal epithelial cells in a thermoreversible polymer (Mebiol Gel) and their transplantation in rabbits: an animal model. Tissue Engineering. Part A. 2009;15(2):407-15. PubMed |
| Vemuganti, Geeta K; Fatima, Anees; Madhira, Soundarya Lakshmi; Basti, Surendra; Sangwan, Virender S. Limbal stem cells: application in ocular biomedicine. International Review Of Cell And Molecular Biology. 275( 19491055):133-81. PubMed |
| Aly, Hussein Hassan; Shimotohno, Kunitada; Hijikata, Makoto. 3D cultured immortalized human hepatocytes useful to develop drugs for blood-borne HCV. Biochemical And Biophysical Research Communications. 2009;379(2):330-4. PubMed |
| Yamamoto, Masamichi; Beppu, Hideyuki; Takaoka, Katsuyoshi; Meno, Chikara; Li, En; Miyazono, Kohei; Hamada, Hiroshi. Antagonism between Smad1 and Smad2 signaling determines the site of distal visceral endoderm formation in the mouse embryo. The Journal Of Cell Biology. 2009;184(2):323-34. PubMed |
| Aly, Hussein H; Watashi, Koichi; Hijikata, Makoto; Kaneko, Hiroyasu; Takada, Yasutugu; Egawa, Hiroto; Uemoto, Shinji; Shimotohno, Kunitada. Serum-derived hepatitis C virus infectivity in interferon regulatory factor-7-suppressed human primary hepatocytes. Journal Of Hepatology. 2007;46(1):26-36. PubMed |
| Sudha, B; Madhavan, H N; Sitalakshmi, G; Malathi, J; Krishnakumar, S; Mori, Y; Yoshioka, H; Abraham, S. Cultivation of human corneal limbal stem cells in Mebiol gel--A thermo-reversible gelation polymer. The Indian Journal Of Medical Research. 2006;124(6):655-64. PubMed |
| Yasuda, Ayuko; Kojima, Koji; Tinsley, Kevin W; Yoshioka, Hiroshi; Mori, Yuichi; Vacanti, Charles A. In vitro culture of chondrocytes in a novel thermoreversible gelation polymer scaffold containing growth factors. Tissue Engineering. 2006;12(5):1237-45. PubMed |
| Medina, Reinhold J; Kataoka, Ken; Takaishi, Mikiro; Miyazaki, Masahiro; Huh, Nam-ho. Isolation of epithelial stem cells from dermis by a three-dimensional culture system. Journal Of Cellular Biochemistry. 2006;98(1):174-84. PubMed |
| Nagaya, Masaki; Kubota, Sunao; Suzuki, Noboru; Akashi, Katsuya; Mitaka, Toshihiro. Thermoreversible gelation polymer induces the emergence of hepatic stem cells in the partially injured rat liver. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.). 2006;43(5):1053-62. PubMed |
| Murakami, Kyoko; Ishii, Koji; Ishihara, Yousuke; Yoshizaki, Sayaka; Tanaka, Keiko; Gotoh, Yasufumi; Aizaki, Hideki; Kohara, Michinori; Yoshioka, Hiroshi; Mori, Yuichi; Manabe, Noboru; Shoji, Ikuo; Sata, Tetsutaro; Bartenschlager, Ralf; Matsuura, Yoshiharu; Miyamura, Tatsuo; Suzuki, Tetsuro. Production of infectious hepatitis C virus particles in three-dimensional cultures of the cell line carrying the genome-length dicistronic viral RNA of genotype 1b. Virology. 2006;351(2):381-92. PubMed |
| Kimura-Yoshida, Chiharu; Nakano, Hiroshi; Okamura, Daiji; Nakao, Kazuki; Yonemura, Shigenobu; Belo, Jose A; Aizawa, Shinichi; Matsui, Yasuhisa; Matsuo, Isao. Canonical Wnt signaling and its antagonist regulate anterior-posterior axis polarization by guiding cell migration in mouse visceral endoderm. Developmental Cell. 2005;9(5):639-50. PubMed |
| Hishikawa, Keiichi; Miura, Shigeki; Marumo, Takeshi; Yoshioka, Hiroshi; Mori, Yuichi; Takato, Tsuyoshi; Fujita, Toshiro. Gene expression profile of human mesenchymal stem cells during osteogenesis in three-dimensional thermoreversible gelation polymer. Biochemical And Biophysical Research Communications. 2004;317(4):1103-7. PubMed |
| Nagaya, M; Kubota, S; Suzuki, N; Tadokoro, M; Akashi, K. Evaluation of thermoreversible gelation polymer for regeneration of focal liver injury. European Surgical Research. Europaische Chirurgische Forschung. Recherches Chirurgicales Europeennes. 2004;36(2):95-103. PubMed |
| Tsukikawa, Satoshi; Matsuoka, Hiromitsu; Kurahashi, Yuko; Konno, Yasushi; Satoh, Koh; Satoh, Ryotaroh; Isogai, Akiko; Kimura, Kanako; Watanabe, Yasuharu; Nakano, Suehiro; Hayashi, Junya; Kubota, Sunao. A new method to prepare multicellular spheroids in cancer cell lines using a thermo-reversible gelation polymer. Artificial Organs. 2003;27(7):598-604. PubMed |
| Shimizu, S; Yamazaki, M; Kubota, S; Ozasa, T; Moriya, H; Kobayashi, K; Mikami, M; Mori, Y; Yamaguchi, S. In vitro studies on a new method for islet microencapsulation using a thermoreversible gelation polymer, N-isopropylacrylamide-based copolymer. Artificial Organs. 1996;20(11):1232-7. PubMed |
| Yoshioka, Hiroshi; Mori, Yuichi; Shimizu, Mitsuhiro. Separation and recovery of DNA fragments by electrophoresis through a thermoreversible hydrogel composed of poly(ethylene oxide) and poly(propylene oxide). Analytical Biochemistry. 2003;323(2):218-23. PubMed |
| Shirasaki, Yoshitaka; Tanaka, Jyunichi; Makazu, Hiroshi; Tashiro, Koichiro; Shoji, Shuichi; Tsukita, Shoichiro; Funatsu, Takashi. On-chip cell sorting system using laser-induced heating of a thermoreversible gelation polymer to control flow. Analytical Chemistry. 2006;78(3):695-701. PubMed |
| Shirasaki, Yoshitaka; Tanaka, Jyunichi; Makazu, Hiroshi; Tashiro, Koichiro; Shoji, Shuichi; Tsukita, Shoichiro; Funatsu, Takashi. On-chip cell sorting system using laser-induced heating of a thermoreversible gelation polymer to control flow. Analytical Chemistry. 2006;78(3):695-701. PubMed |
| Arai, Takao; Joki, Tatsuhiro; Akiyama, Masaharu; Agawa, Miyuki; Mori, Yuichi; Yoshioka, Hiroshi; Abe, Toshiaki. Novel drug delivery system using thermoreversible gelation polymer for malignant glioma. Journal Of Neuro-Oncology. 2006;77(1):9-15. PubMed |