Product Description
The Magnetic Cell separation Kit for Human CD44v9+ Cancer Stem Cell is a magnetic particle that binds a monoclonal antibody that binds with high affinity to the membrane antigen CD44v8-10, which is highly expressed in cancer stem cells, by using magnetic separation. Can enrich cancer stem cells.
Background
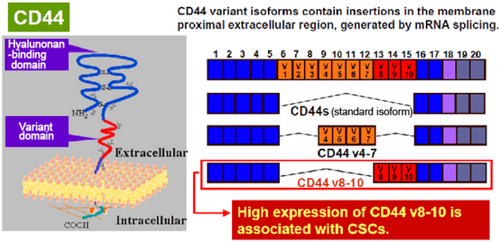
In recent years, it has become clear that cancer stem cells are the source of canceration, such as the formation of cancerous tissue, its metastasis, and recurrence. Therefore, it is considered necessary to eliminate cancer stem cells in order to eradicate cancer, and cancer stem cells are drawing attention as the ultimate target for cancer treatment. However, cancer stem cells are present in tissues and cell lines in extremely small amounts (less than a few percent), so it has been difficult to develop therapeutic drugs targeting them and study their functional analysis.
"Anti-CD44v antibody" is a monoclonal antibody that binds with high affinity to the membrane antigen CD44v8-10, which is frequently expressed in cancer stem cells, and it has been difficult to use cancer stem cells by using a cell sorter. Concentration can be easily achieved. By enriching cancer stem cells, it is possible to construct a "sphere culture system" used as an in vitro evaluation system for cancer stem cells and a "mouse lung metastasis model" used as an in vivo evaluation system. It will be possible to elucidate the mechanism of cancer development and metastasis and to screen therapeutic agents for cancer stem cells. The "anti-CD44v antibody" will be a powerful tool for developing new therapeutic agents targeting cancer stem cells.
Features
- Can easily enrich cancer stem cells with magnetic particles bound with cancer stem cell marker antibody
- Collecting cancer stem cells by a simple operation using a magnetic stand without using FACS
- Separated cells can be used for flow cytometric analysis
Kit Contents
- anti-CD44v9 magnetic beads (RV3 beads)
- Binding buffer
- Wash buffer
Workflow
Experimental Example
Isolate cells expressing CD44v9-GFP stably and analyze by flow cytometry
Figure 1. Ratio of CD44v9- expressing cells in RV3 bead-positive cells Stable expressing cells in which CD44v9-GFP was introduced into 293F cells and parent cell line 293F cells were mixed at any ratio (A, B, C). Was isolated using this product. CD44v9 expressing cells were concentrated from 4.97% (A), 15.3% (B) and 55.7% (C) before separation to 86.4% (A), 97.1% (B) and 99.0% (C) after separation.
Separation of cancer cells and analysis by flow cytometry
Figure 2. Ratio of CD44v9-expressing cells in RV3 bead-positive cells RV3 bead-positive cells were stained with PE-labeled anti-rat IgG antibody and analyzed by flow cytometry. Also in the human prostate cancer cell line PC-3 (A) and the human pancreatic adenocarcinoma cell line AsPC-1 (B), the ratio of CD44v9-expressing cells was increased compared to that before the isolation.
| Documents & Links for Magnetic Cell separation Kit for Human CD44v9+ Cancer Stem Cell | |
| Datasheet | Magnetic Cell separation Kit for Human CD44v9+ Cancer Stem Cell Datasheet |
| Documents & Links for Magnetic Cell separation Kit for Human CD44v9+ Cancer Stem Cell | |
| Datasheet | Magnetic Cell separation Kit for Human CD44v9+ Cancer Stem Cell Datasheet |
| Citations for Magnetic Cell separation Kit for Human CD44v9+ Cancer Stem Cell – 1 Found |
| Aguilar-Chaparro, Mario Alejandro; Rivera-Pineda, Sonia Andrea; Hernández-Galdámez, Hury Viridiana; Piña-Vázquez, Carolina; Villa-Treviño, Saúl. The CD44std and CD44v9 subpopulations in non-tumorigenic invasive SNU-423 cells present different features of cancer stem cells. Stem Cell Research. 2023;72( 37844417):103222. PubMed |





