AteloGene Systemic Use
Cosmo Bio
- SKU:
- KOU-1393
- Shipping:
- Calculated at Checkout
Agreement for purchasing AteloGene:
Please fill out the agreement form (PDF file located in Documents tab), then fax or e-mail the completed form to Cosmo Bio USA prior to placing your order with us.
See also:
AteloGene for Local Use, Quick Gelation
This product is a kit for delivering siRNA into live mice.
Principle:
When mixed with synthetic siRNA at an appropriate concentration and ratio, atelocollagen, which is a major component of “AteloGene” forms a complex appropriate for administration into the body. siRNA that is prepared into a complex with atelocollagen is efficiently delivered in vivo and introduced into the cells.
Features & Advantages:
- Prolonged RNAi effect because atelocollagen, the main component of “AteloGene”, forms complexes with siRNA/miRNA.
- Since “AteloGene” is made from atelocollagen, it is nontoxic.
- Immediate administration to experimental animals by mixing the synthetic siRNA with “AteloGene”.
- Efficient in vivo transfection of siRNA.
- The effect of RNAi of preventing degradation by RNase persists for a long time.
- “AteloGene” has no toxicity, and its main component is atelocollagen that demonstrates high biological compatibility
- It is possible to choose “AteloGene Local Use” for local administration or “AteloGene Systemic Use” for systemic administration by injection to the tail vein
- Since “AteloGene Local Use” for local administration is gelated in the body, siRNA is securely kept at the administration site
- Since “AteloGene Systemic Use ” for systemic administration is not gelated in the body but circulated in the blood after injection into the tail vein, siRNA is efficiently delivered to the whole body.
Application:
Mechanism of siRNA transfection using “ AteloGene” Mechanism
Local administration
Experimental Example 1:
Suppression of gene expression of subcutaneous tumor in mice
When luciferase siRNA (Luc siRNA) was administered using "AteloGene" against luciferase-expressing tumor cells that were subcutaneously grafted, the luciferase expression was inhibited at a larger degree compared with results observed after the administration of Luc siRNA alone.
Experimental Example 2:
Stability of VEGF siRNA by intratumoral administration
(Date source: Dr. Y. Takei, Nagoya University, Japan)
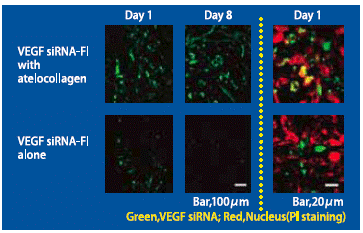
AteloGene Local Use was mixed with fluorescent labeled vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) siRNA and injected into subcutaneous tumor. Compared to VEGF siRNA alone, siRNA complexed with Atelogene was efficiently delivered to tumor cells. Remarkably, VEGF-siRNA was present 8 days following administration and tumor growth was inhibited.
Reference : Takei Y, et al. A small interfering RNA targeting vascular endothelial growth factor as cancer therapeutics. (2004) Cancer Res. 64(10):3365-3370.
Experimental Example 3:
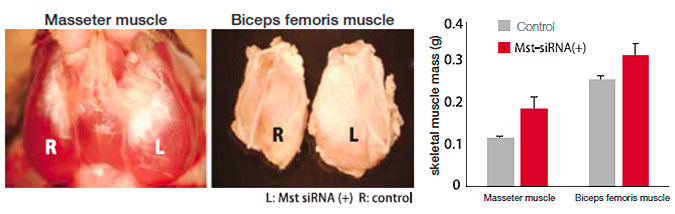
siRNA targeting Myostatin (Mst), an inhibitor of muscle differentiation, was injected intramuscularly in complex with Atelogene Local Use. Muscular mass was significantly increased in animals receiving Mst siRNA. Increased muscular mass was also observed following systemic injection of Mst specific siRNA/AteloGene Systemic Use complexes
Reference : Kinouchi N, et al. Atelocollagen-mediated local and systemic applications of myostatin-targeting siRNA increase skeletal muscle mass. (2008) Gene Ther. 15(15):1126-1130.
Systemic administration:
Suppression of gene expression of generalized metastasized tumors in mice.
When luciferase siRNA (Luc siRNA) was administered using "AteloGene" against luciferase-expressing generalized metastasized tumor cells, the luciferase expression was more inhibited compared with the result observed after the administration of Luc siRNA alone.
| Documents & Links for AteloGene Systemic Use | |
| Datasheet | kou-1393_atelogene-systemic-use_datasheet.pdf |
| Purchase Agreement | AteloGene Systemic Use Purchase Agreement |
| Documents & Links for AteloGene Systemic Use | |
| Datasheet | kou-1393_atelogene-systemic-use_datasheet.pdf |
| Purchase Agreement | AteloGene Systemic Use Purchase Agreement |
| Citations for AteloGene Systemic Use – 1 Found |
| Shitashige, Miki; Satow, Reiko; Jigami, Takafumi; Aoki, Kazunori; Honda, Kazufumi; Shibata, Tatsuhiro; Ono, Masaya; Hirohashi, Setsuo; Yamada, Tesshi. Traf2- and Nck-interacting kinase is essential for Wnt signaling and colorectal cancer growth. Cancer Research. 2010;70(12):5024-33. PubMed |


