Product Summary
Dementia is a disease that causes memory and judgement loss, there is no fundamental treatment developed for it. Years of scientific research has proven that protein aggregation occurs in the degeneration part of the brain for many neurodegenerative diseases including dementia, indicating appearance of this aggregation is closely related to these diseases development and progression. Aggregation occurs when normal protein forms abnormal structure for particular reasons and accumulates in the cell, which each disease has different aggregating protein. It is known that protein called “ α -Synuclein“ forms abnormal structure in Parkinson Disease / Lewy Body Dementia / Multiple system atrophy patient brain. α -Synuclein Aggregation Assay Kit mimics intracellular aggregation of “ α -Synuclein“, which allows in vitro screening of active ingredients.
Amyloid protein aggregates in brain neruonal and glial cells are a hallmark of several human neurodegenerative diseases. In Parkinson disease and dementia with Lewy bodies patients, for example, fibrilar a-synuclein protein is the major aggregate component and it is believed that these aggregates are related to disease etiology.
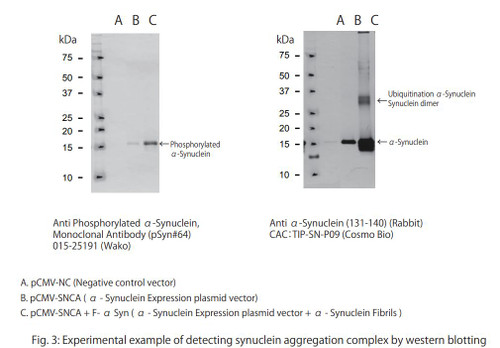
Overexpression of a-synuclein in cells by plasmid transfection alone does not result in a-synuclein aggregation. However, as described by Nonaka et. al. (1) co-transfection of plasmid with preformed a-synuclein protein fibrils into SH-SY5Y (neuroblastoma-derived) cells results in the rapid formation of phosphorylated, ubiquitinated and partially thyoflavin positive a-syn fibrilar aggregates that are mophologically and physicochemically similar to those in patient brain.
This kit contains all critical reagents needed to peform the seeded aggregation technique of Nonoka et al in your lab, with the cells of your choice, enabling a-synuclein aggregate formation to be studied kinetically, structurally, pathologically, or in response to biological and chemical manipulation.
References
(1) Nonaka T, Watanabe ST, Iwatsubo T, Hasegawa M. Seeded aggregation and toxicity of {alpha}-synuclein and tau: cellular models of neurodegenerative diseases. J Biol Chem. 2010 Nov 5;285(45):34885-98. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.148460. Epub 2010 Aug 30. PMID: 20805224; PMCID: PMC2966103.
| Kit Components | Volume | Quantity |
| pCMV-SNCA (α - Synuclein Expression plasmid vector, Red cap) (conc. 1.25 μg/μL) |
32 µL (conc. 1.25 µg/µL) | 1 vial |
| pCMV-NC(Negative control vector, Green cap) | 5 µL (conc. 1.25 µg/µL) | 1 vial |
| pCMV-dGFP (dGFP Expression plasmid vector, Blue cap) | 5 µL (conc. 1.25 µg/µL) | 1 vial |
| 20 mM Tris-HCl Buffer (pH7.4) | 10mL | 1 bottle |
| F- α Syn ( α - Synuclein Fibrils, Yellow cap) | 32 µL (conc. 1 µg/µL) | 1 vial |
| Multifectam (Gene transfection reagent) | 0.33 mg | 1 bottle |

Related Products
| Documents & Links for Alpha-Synuclein Aggregation Assay Kit | |
| Datasheet | Alpha-Synuclein Aggregation Assay Kit Datasheet |
| Documents & Links for Alpha-Synuclein Aggregation Assay Kit | |
| Datasheet | Alpha-Synuclein Aggregation Assay Kit Datasheet |
| Citations for Alpha-Synuclein Aggregation Assay Kit – 3 Found |
| Fujii, Takuto; Nagamori, Shushi; Wiriyasermkul, Pattama; Zheng, Shizhou; Yago, Asaka; Shimizu, Takahiro; Tabuchi, Yoshiaki; Okumura, Tomoyuki; Fujii, Tsutomu; Takeshima, Hiroshi; Sakai, Hideki. Parkinson's disease-associated ATP13A2/PARK9 functions as a lysosomal H(+),K(+)-ATPase. Nature Communications. 2023;14(1):2174. PubMed |
| Suzuki, Genjiro; Imura, Sei; Hosokawa, Masato; Katsumata, Ryu; Nonaka, Takashi; Hisanaga, Shin-Ichi; Saeki, Yasushi; Hasegawa, Masato. α-synuclein strains that cause distinct pathologies differentially inhibit proteasome. Elife. 2020;9( 32697196) PubMed |
| Nonaka, Takashi; Watanabe, Sayuri T; Iwatsubo, Takeshi; Hasegawa, Masato. Seeded aggregation and toxicity of {alpha}-synuclein and tau: cellular models of neurodegenerative diseases. The Journal Of Biological Chemistry. 2010;285(45):34885-98. PubMed |