In 1957, O. Mäkelä classified them into 4 groups according to the coordination of the hydroxyl groups at the C-3 and C-4 positions of the sugar (Table 1). Lectins classified in the 4th county have not been found yet. Recently, the primary structure of lectins has been analyzed, and classification based on that structure (classification by family) has also been performed (Table 2).
Table 1 Classification of lectins based on monosaccharide recognition in Mäkelä
| Classification of Mäkelä | origin | Lectin trivial name | Sugar binding specificity | My Togen activity |
Fuc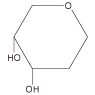 |
Gorse | UEA-I | α-L-Fuc | - |
| Gal GalNAc 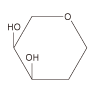 |
Soybean Peanuts Ricinus castor (Ricinus communis) Dorikosumame Mushroom Green beans |
SBA PNA RCA120 DBA ABA PHA-E PHA-L |
α-GalNAc> β-GalNAc β-Gal β-Gal α-GalNAc Gal β1-3GalNAc GalNAc GalNAc |
+ ± - - + |
| D-Man D-Glc 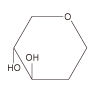 D-GlcNAc |
Sword bean pea lentil lentil broad bean Pokeweed potato wheat germ gorse |
Con A PSA LCA VFA PWM STA WGA UEA-II |
α-Man > α-Glc α-Man > α-Glc α-Man > α-Glc α-Man > α-Glc GlcNAcβ1-4GlcNAc GlcNAcβ1-4GlcNAc GlcNAcβ1-4GlcNAc GlcNAcβ1-4GlcNAc |
+ + + + + ± - |
| L-Glc L-Man 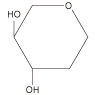 |
- | - | - | - |
Table 2 Classification of lectins by family
| Family (biological distribution) | Sugar specificity | Main lectins |
| Leguminosae Lectin L-type lectin (plant) |
Man Gal Sia Fuc | DSA PHA SBA UEA-I MAM DBA ConA ECA PSA |
| Monocot lectin M-type lectin (plant) |
Mab | GNA HHA ASA |
| R-type lectin (animals and plants) |
Man Gal Sia Xyl | RCA 120 SSA SNA |


