Human breast milk-derived exosomes
Useful for studying the function of exosomes in breast milk and their mechanism of action
This product is an exosome fraction prepared by ultracentrifugation from breast milk ethically provided by healthy humans. It can be used for a wide range of experiments from in vitro to in vivo . Raw material breast milk has been confirmed to be free of infectious diseases (HIV-1, HCV, HBV by NAT, HBsAg, HCV Ab, HIV 1 and 2 Ab, RPR) by FDA approved methods.
Background
Exosomes are membrane vesicles with a diameter of about 50 nm to 150 nm that are secreted by most cells. It has also been confirmed to be secreted from These exosomes contain miRNAs, mRNAs, proteins, micropeptides, etc., and have been suggested to play a role in transmitting information from the cell or tissue of origin to another target cell or tissue1 . Targeting has not yet been fully clarified. On the other hand, it is known that cancer metastasis can be suppressed by neutralizing signal transduction by exosomes with antibodies specific to exosome surface antigens such as CD9 and CD63. 2 Exosomes are also present in human breast milk and have been found to express exosome markers such as CD63 and CD81. 3 Exosomes in human breast milk contain many miRNAs, among which many miRNAs related to immunity have been identified, suggesting the possibility that these miRNAs are transferred from mothers to infants. 4There are several reports on the regulation of immune cells by exosomes in human breast milk3,5, while porcine milk-derived exosomes have also been reported to exert direct growth-promoting functions on infant intestinal epithelial cells. Yes 6 , research on the functions of exosomes in breast milk and their mechanisms of action has attracted attention.
Product data
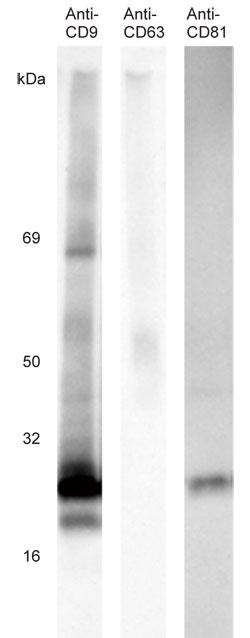
Fig. 1 Western blotting using CD9, 63, 81 monoclonal antibody Using
0.5 µg as protein amount, Anti-CD9 monoclonal antibody (Part number: SHI-EXO-M01), Anti-CD63 monoclonal antibody (Part number: SHI-EXO -M02) and Anti-CD81 monoclonal antibody (product number: SHI-EXO-M03).
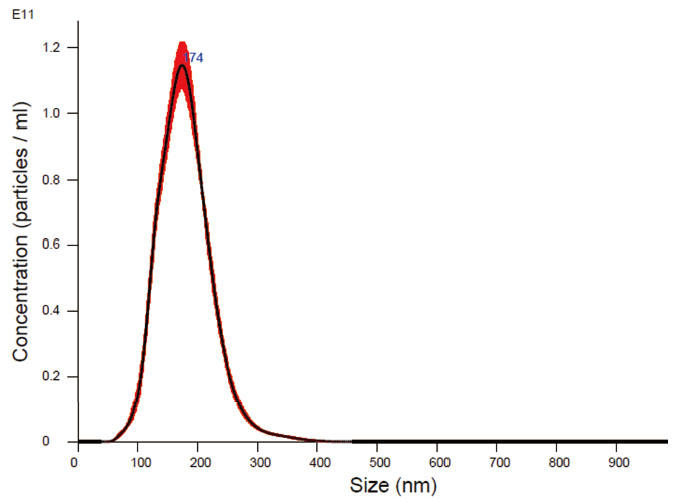
Fig.2 Particle size distribution measurement using NanoSight
This product was diluted 200 times with PBS and measured with NanoSight LM10.
Average particle size: 179
nm Number of particles per mL of this product: 2.3 × 10 12 Particles
* The number of exosome particles varies by lot. Please refer to the CoA attached to the product.
References
- Tumor exosome integrins determine organotropic metastasis, Hoshino A, et al ., Nature . 2015 Nov 19; 527 (7578): 329-35.
- Disruption of Circulating Extracellular Vesicles as a Novel Therapeutic Strategy against Cancer Metastasis, Nao Nishida-Aoki, et al ., Mol Ther . 2017 Jan 4; 25 (1): 181-191.
- Exosomes with Immune Modulatory Features Are Present in Human Breast Milk, Charlotte A, et al ., J Immunol August 1, 2007, 179 (3) 1969-1978.
- microRNA as a new immune-regulatory agent in breast milk, N Kosaka, et al ., Silence . 2010 Mar 1; 1 (1):7
- Exosomes from breast milk inhibit HIV-1 infection of dendritic cells and subsequent viral transfer to CD4+ Tcells, Näslund TI et al ., AIDS . 2014 Jan 14; 28 (2):171-80.
- Porcine milk-derived exosomes promote proliferation of intestinal epithelial cells, T Chen, et al ., Scienti_c Reports volume 6, Article number: 33862 (2016)
Human breast milk-derived exosomes
| Catalog Number | Product Name | Size |
| CSR-EXHM100L | Breast Milk Exosome, Human | 1 ml |
* The number of exosome particles varies from lot to lot. Please refer to the CoA attached to the product.
* Raw human milk is ethically justified and provided by consenting and dedicated donors.
* Source breast milk has been confirmed to be free of infectious diseases (HIV-1, HCV, HBV by NAT, HBsAg, HCV Ab, HIV 1 and 2 Ab, RPR) by FDA approved methods.
