- CAC Antibody Collection Index Page
Antibody Group
Advanced glycation end products (AGEs)
Autophagy and apoptosis
Bacteria-related
Calcium-binding proteins
Cancer
CD44 for enriching cancer stem cells
Tumor markers
Tumor inhibitors
Chaperones
Cytoskeleton
DNA damage
UV-induced DNA lesions
8-Nitroguanosine for oxidative stress research
Nucleotide excision repair factors
Epigenetics and chromatin
Histone H3 variants
Post-translationally-modified histone H3
Chromatin structure modifiers
Drosophila chromatin
Epitope tags
Exosomes
Extracellular matrix
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs)
Proteoglycans
Matrix and basement membrane
Cell adhesion and hemidesmosome-related
Bone and cartilage-related
Wound repair-related
Hedgehog pathway
Hormones
Immunology
Fish CD4 and CD8α
Allergic disease-related
Adaptive and innate immunity
Macrophages
Inflammatory cytokines
Viral recognition pathways
Vpr for HIV research
Insulin-like growth factor-related
Mitochondria-related
Neurobiology
Neurodegenerative disease markers
Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors
Miscellaneous
Nuclear import and export
Oxidative stress
Plant-related
Plant hormones
Plant autophagy and apoptosis
Plant stress response
Plant stress response
Proteasomes
Puromycin-specific
Reproductive biology
Small molecules
Stem cells
Novel iPS/ES markers
Pluripotency-associated
Sumoylation pathway
TGF-beta pathway
TGF-beta LAP-d
TGF-beta signaling
Transcription factors
Transporters
Tyrosine phosphatases
Ubiquitin-Proteasome Related
 CAC Antibody Collection
CAC Antibody Collection
The antibodies on this page are part of Cosmo Bio's exclusive CAC Collection. For many many thousands of other antibodies from many different makers, use our Search the Store function and our Explore Products drop down menu.
Sumoylation pathway
SUMOylation is a reversible post-translational modification which has emerged as a crucial molecular regulatory mechanism, involved in the regulation of DNA damage repair, immune responses, carcinogenesis, cell cycle progression and apoptosis. Four SUMO isoforms have been identified, which are SUMO1, SUMO2/3 and SUMO4. The small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) pathway is conserved in all eukaryotes and plays pivotal roles in the regulation of gene expression, cellular signaling and the maintenance of genomic integrity. The SUMO catalytic cycle includes maturation, activation, conjugation, ligation and de-modification. The dysregulation of the SUMO system is associated with a number of diseases, particularly cancer. SUMOylation is widely involved in carcinogenesis, DNA damage response, cancer cell proliferation, metastasis and apoptosis. SUMO can be used as a potential therapeutic target for cancer. [from: Han ZJ, Feng YH, Gu BH, Li YM and Chen H. (2018) The post-translational modification, SUMOylation, and cancer (Review). International Journal Of Oncology. 52:1081-1094.]| Product name (click for order info) | Cat No (click for datasheet) |
Host | Species specificity |
| Anti Small Ubiquitin-Related Modifier 2 (SUMO2) and Small Ubiquitin-Related Modifier 3 (SUMO3) mAb (Clone 3H12) | CAC-CE-044 | RT | HU MS RT MKY |
| Product name | Anti Small Ubiquitin-Related Modifier 2 (SUMO2) and Small Ubiquitin-Related Modifier 3 (SUMO3) mAb (Clone 3H12) |
| Cat No | CAC-CE-042A |
| Description | SUMO is a Ubiquitin-like protein that can be covalently attached to proteins as a monomer or a lysine-linked polymer. This post-translational modification on lysine residues of proteins plays a crucial role in a number of cellular processes such as nuclear transport, DNA replication and repair, mitosis and signal transduction. References: 1) Saitoh et al. (2006). Exp Cell Res. 312:1418-1430. This antibody is used in ref.1. |
| Host | RT |
| Species specificity | HU MS RT MKY |
| Figure 1 | 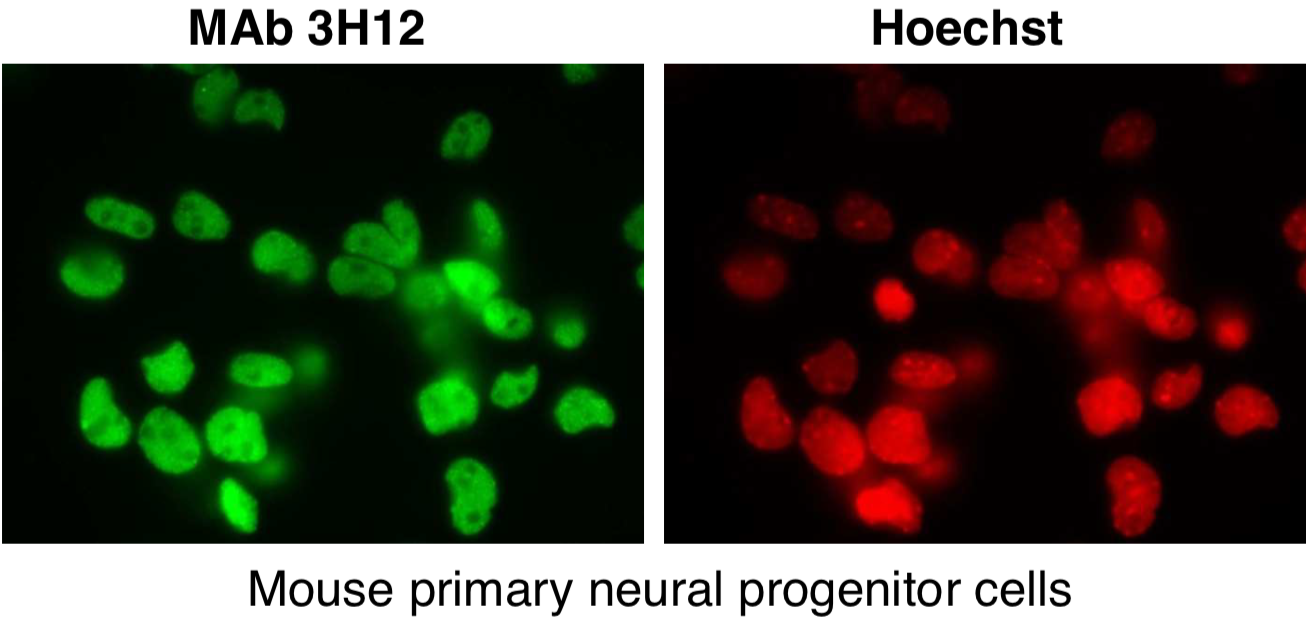 |
| Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence analysis of SUMO2/3 antibody (3H12) on mouse primary culture neurons. | |
| Figure 2 | 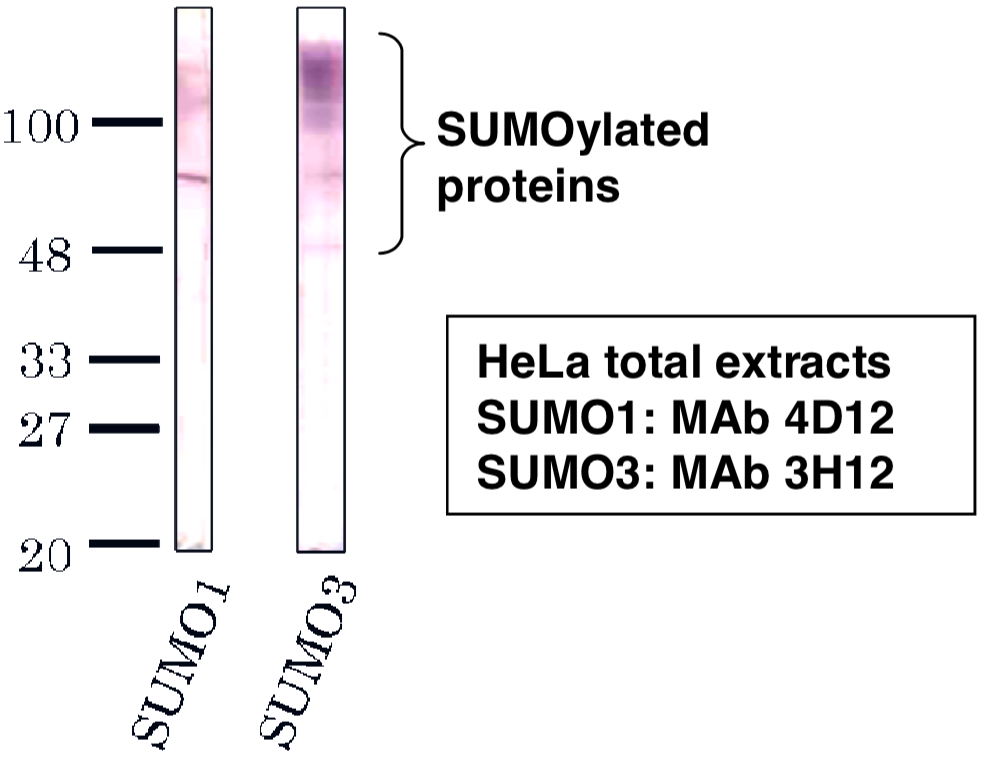 |
| Immunoblot analysis of SUMO1 antibody (4D12) and SUMO3 antibody (3H12) on HeLa cell extracts. |
