Confocal Science (CFS) : C-Kit Ground Pro XRD
To grow high quality protein crystals
C-Kit Ground Pro XRD
|
Principle of counter-diffusion method
The counter-diffusion method is a crystallization method in which the protein sample and the crystallization reagent are mutually diffused in the capillary. Protein molecules diffuse from the inside to the outside of the capillary, and crystallization reagent molecules diffuse from the outside to the inside of the capillary, forming a concentration gradient within the capillary. A wide range of concentration conditions is realized in the capillary over time, and crystal growth starts when the crystal growth conditions are realized. Therefore, by setting the concentration of the crystallization reagent in the external solution high, it is possible to easily search for a wide range of crystallization conditions. In other words, with the counter-diffusion method, you are screening an infinite number of crystallization conditions in a single capillary.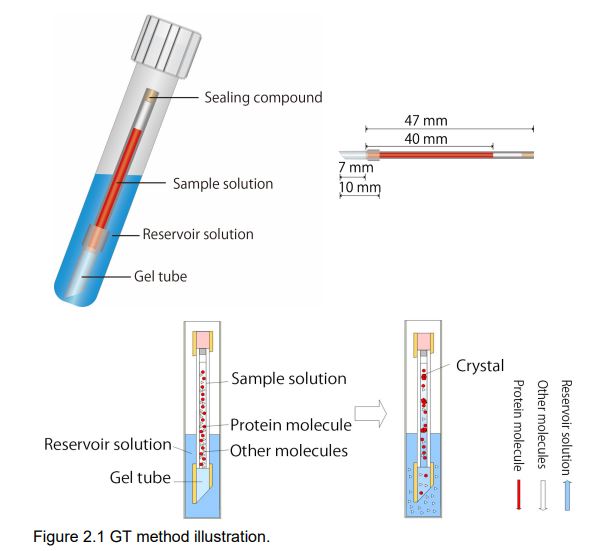
| Catalog Number | Product Name | Size |
| CFS-CRT101-1 | C-Kit GroundPro (XRD) | 1 Set |
| Item | Quantity | Counter diffusion method (CD) | Diffusion pair under osmotic concentration method (DPOC) | Details |
| Capillary | 15 | 〇 | Glass capillary (ID 0.5 mm, OD 1.2 mm, length 47 mm). | |
| Gel-tube | 18 | 〇 | ID 1 mm, OD 2 mm, length 10 mm | |
| 5mL test tube | 23 | 〇 | 〇 | For incubating loaded samples |
| DPOC-tube | 8 | 〇 | Silicon tube (ID 1.0 mm, OD 2.0 mm, length 39.5 mm) without an osmo-resistant cover. | |
| C-Cap | 16 | 〇 | For protect DPOC-tube ends from osmotic pressure. | |
| Silicon-tube | 50cm | 〇 | For sample loading | |
| Instruction Manual | 1 | 〇 | 〇 | |
| Sealing compound | 1 | 〇 | 〇 |
References
1) Tanaka, Hiroaki, et al. "A simplified counter diffusion method combined with a 1D simulation program for optimizing crystallization conditions." Journal of synchrotron radiation 11.1 (2004): 45-48.
2) Takahashi, Sachiko, et al. "JCB-SGT crystallization devices applicable to PCG experiments and their crystallization conditions." International Journal of Microgravity Science and Application 36.1 (2019): 360107.

