Schwann cells are cells that form and maintain the myelin sheath that surrounds the axons of peripheral nerves, and also produce cytokines that are important for the maintenance of motor and sensory neurons. In recent years, it has become clear that Schwann cells play a major role in axonal guidance and repair in the process of axonal regeneration after nerve injury. Abnormalities in Schwann cells have also attracted attention as a causative factor of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
Product data
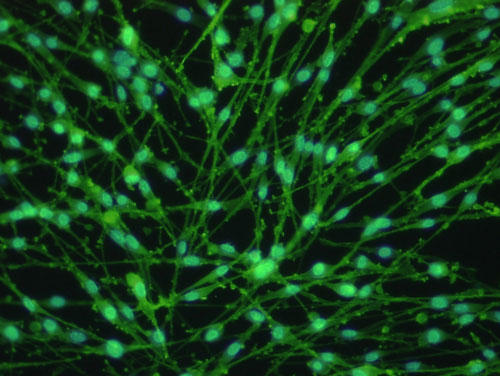
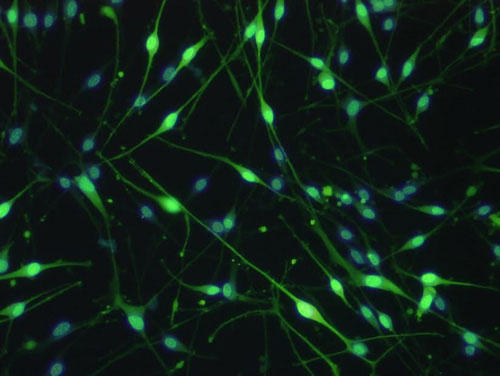
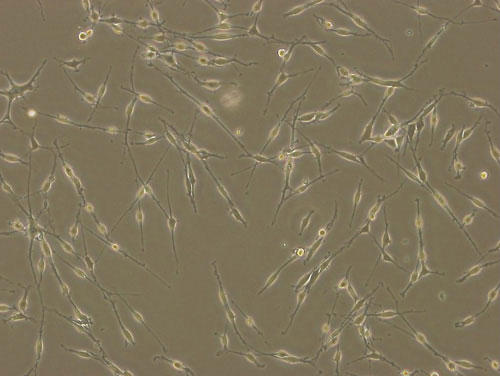
Figure 1. Fluorescent immunostaining and phase-contrast microscope image
Left) Anti-p75 antibody fluorescent staining (green: p75, blue: nuclear staining)
Center) Anti-S100 antibody fluorescent staining (green: S100, blue: nuclear staining)
Right) Phase-contrast microscope image
Magnification: X100
- Sango K, Yanagisawa H, Kawakami E, et al. Spontaneously immortalized Schwann cells from adult Fischer rat as a valuable tool for exploring neuron-Schwann cell interactions. J Neurosci Res 2011;89:898-908.
- Sango K, Kawakami E, Yanagisawa H, et al. Myelination in coculture of established neuronal and Schwann cell lines. Histochem Cell Biol 2012;137:829-839.
- Sango, Kazunori, et al. "Immortalized adult rodent Schwann cells as in vitro models to study diabetic neuropathy." Experimental diabetes research 2011