Cell / Cell culture products
Astrocytes(rats and mice)
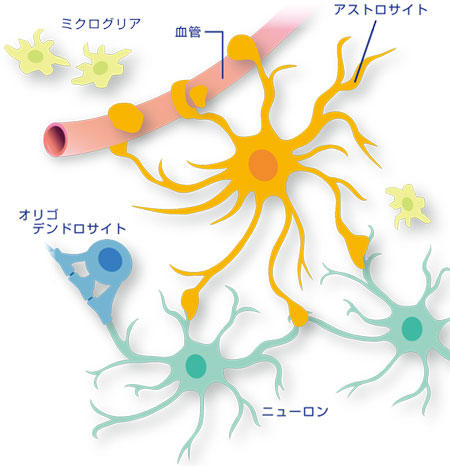
In recent years, it is known that glial cells (microglia, astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, etc.) in the brain not only play a static role in maintaining homeostasis of brain function, but also actively work to control brain function.
We offer a variety of glial cells, including astrocytes, primary microglia isolated in a mixed culture system, and new established microglia that can reproduce the in vivo morphology. Please use it for your glial cell research.
Background
Heterogeneous Role of glial cells: Neurotoxicity or Neuroprotection
Astrocytes are the most numerous glial cells in the brain, and their main functions have been thought to be maintenance of nerve fibers, homeostasis, and blood-brain barrier closure. However, astrocytes are known to cause morphological changes such as Alzheimer's type 2 astrocytes and fibrous astrocytes due to inflammation, liver damage, neurodegeneration, etc., and eventually form gliosis. In addition, stimulation by cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF-α), interleukin (IL)-1β and interferon (IFN) γ increases the production of arachidonic acid metabolites, reactive oxygen species (ROS) and nitric oxide (NO). 1) , etc., have been shown to have neurotoxic effects. On the other hand, it has also been shown to exhibit neruroprotective effects, such as anti-oxidant effect 2) by secretion of glutathione (GSH) in Parkinson's disease, and control of synaptic transmission by release of neurotransmitters such as glutamic acid, ATP, and D-serine 2) .
It has been thought that the main function of microglia is to remove degenerated cells by phagocytosis of antigen-presenting cells and macrophages during inflammation. IFNγ-positive microglia have been confirmed 3) , and while they have neurotoxic aspects such as ROS and NO production, activated microglia cooperate with the aforementioned astrocytes to release nerve growth factor (NGF), neurotrophin, Secretes neuroprotective factors such as IL-6 and promotes neurogenesis from stem/progenitor cells4 )It is also believed to act as a neruroprotective. As mentioned above, microglia and astrocytes are now thought to have heterogeneous aspects, and many aspects of the complex functions of glial cells under various environments are still unclear. Expected.
- Blasko, I., Stampfer-Kountchev, M., Robatscher, P., Veerhuis, R., Eikelenboom, P., & Grubeck-Loebenstein, B. (2004). Aging cell , 3(4), 169 -76.
- Maragakis, NJ, & Rothstein, JD (2006). Nature clinical practice Neurology , 2(12), 679-89.
- Sawada, M. (2009). Parkinsonism & related disorders , 15 Suppl 1, S39 41.
- Johansson, C., Momma, S., & Clarke, D. (1999). Cell , 96, 25-34.
Composition
| Animal | Organization | Age in weeks | Capacity | Catalog Number |
| SD rat | brain | Fetus 18-20 days old | 1×10 6 cells/vial |
PMC-AST01C
frozen cells |
| C57BL/6N mice | fetus 16-17 days old | 1× 10 6 cells/vial |
PMC-AST02C
frozen cells |
Frozen Cells : The cells are delivered frozen in dry ice packaging. You can take it out immediately after delivery and start culturing immediately, or you can freeze it at the temperature specified in the instruction manual.
Example of use
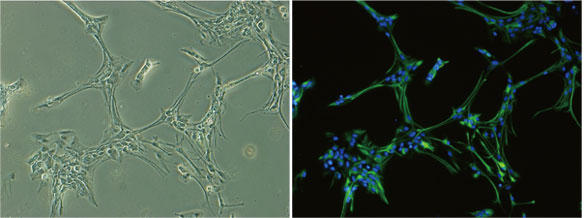
Left: Cell morphology of cultured rat astrocytes
Right: Immunostaining of cultured rat astrocytes (green: anti-GFAP antibody staining, blue: nuclear staining)
Astrocyte cells (frozen cells)
Cells are confirmed to be GFAP positive.
This product was developed under the guidance of Associate Professor Mari Yamanohata, Faculty of Engineering, Soka University.
| Catalog Number | Product Name | Size |
| PMC-AST01C | Astrocytes (rat) | 1 Vial |
| PMC-AST02C | Astrocytes (mouse) | 1 Vial |
- If the frozen cells will not be used immediately after receipt, store them in liquid nitrogen (or below -70°C).
- Please use the cells together with the dedicated medium.
Recommended Medium
| Catalog Number | Product Name | Size |
| PMC-ASTM | Astrocyte Culture medium | 250 ml |
