Elastin Anti-Glycation Assay Kit (Glyceraldehyde)
Lifestyle-related diseases/Aging prevention research/Development of functional materials with a focus on blood vessels and ligaments
The Elastin Anti-Glycation Assay Kit (Glyceraldehyde) is a kit that allows you to follow the glycation reaction of elastin in a cell-free and non-enzymatic manner using a 96-well plate. By using glyceraldehyde, a sugar metabolism intermediate, it is possible to screen for substances that inhibit the glycation reaction of elastin in a shorter period of time.
Please use it for lifestyle-related disease and anti-aging research and functional material development focusing on blood vessels and ligaments.
Background
Saccharides are essential nutrients for life activities, but when they coexist with proteins in the body, they modify lysine and arginine residues in proteins to form crosslinks, change the three-dimensional structure of proteins, and greatly affect activity and physical properties. increase. This reaction is called the glycation reaction (Glycation) or the Maillard reaction. reactions can be divided.
Elastin, along with collagen, is one of the extracellular matrices, and contains many hydrophobic amino acids, including alanine, glycine, valine, and proline. Elastin is an elastic fibrous protein that is abundantly distributed in the aorta, ligaments, lungs, skin, connective tissue, etc. In vivo, it coils around collagen (Fig. 1) and maintains the shape of the tissue, resulting in elasticity and stretchability. is giving A large amount of elastin is contained in the medial portion of the vascular wall, and the content is higher in arteries that are thicker and subject to higher blood pressure. Elastin maintains the elasticity and flexibility of blood vessels (Fig. 2).
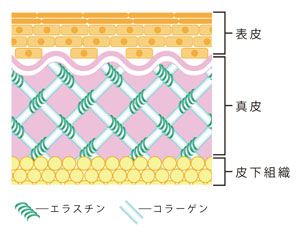
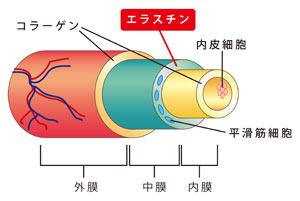
Figure 1 (left) Elastin in skin tissue
Figure 2 (right) Elastin in arterial wall
It has been reported that elastin in blood vessel walls and skin tissue also undergoes glycation due to aging and diseases such as diabetes, causing hardening and aging of blood vessels and skin.
Intended use
This kit is suitable for searching for anti-glycation components using the fluorescence emitted from the glycated elastin solution (excitation wavelength: 370 nm, fluorescence wavelength: 440 nm) as an indicator.
Composition
This kit is capable of assaying two 96-well plates.
| content | capacity | quantity |
| elastin solution | 10 mL | One |
| Glyceraldehyde solution (500 mM) | 2mL | One |
| buffer | 30 mL | One |
| Aminoguanidine solution (20 mM) | 0.5mL | One |
| *Anti-glycation standard substance |
Things to prepare (Other necessary things)
- For measurements using 96-well plates, a 96-well black plate (sterile) is required.
(Greiner μCLEAR®-PLATE BLACK part number: 655090 or equivalent) - A fluorescence plate reader (370 nm excitation, 440 nm emission) is required.
μCLEAR® is a registered trademark of Greiner Bio-One.
Measuring method
- Elastin solution should be brought to room temperature before use.
- Dispense 50 μL of elastin solution per well into a 96-well plate.
- Dissolve or extract the test sample with buffer solution, filter-sterilize with a filter (pore size 0.22 μm), and add 40 μL to the well containing the elastin solution.
- For the positive control, prepare a 5-fold dilution series of aminoguanidine solution (20 mM) with buffer solution, and add 40 μL to wells containing elastin solution.
- Add 10 μL of 500 mM glyceraldehyde solution to all wells, close the lid (seal) of the plate, and stir with a plate mixer.
Addition of glyceraldehyde solution initiates saccharification. - Measure the fluorescence intensity at an excitation wavelength of 370 nm and an emission wavelength of 440 nm with a fluorescence plate reader within 5 minutes after adding the glyceraldehyde solution. Let this measured value be the fluorescence intensity A at 0 hours of reaction.
- Place the plate in a 37°C incubator under moist conditions (Caution 1) for 3-6 days to prevent the solution from drying out. The longer the reaction period, the more saccharification progresses.
- Measure the fluorescence intensity at an excitation wavelength of 370 nm and an emission wavelength of 440 nm using a fluorescence plate reader. Let this measured value be fluorescence intensity B.
- Let the saccharification degree of each well be fluorescence intensity B - fluorescence intensity A.
Example
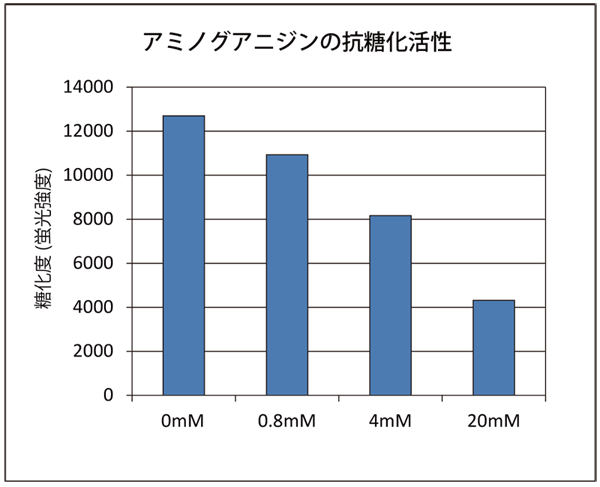
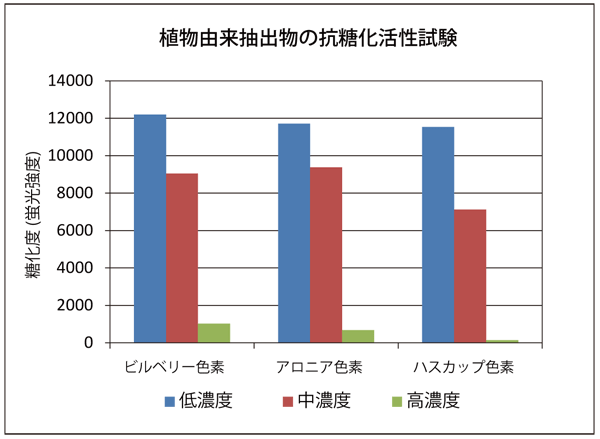
The anti-glycation activity of aminoguanidine, which is an anti-glycation reference substance, and the plant-derived extract were investigated (results on day 3 of saccharification are shown). It was confirmed that each sample had concentration-dependent anti-glycation activity. However, the concentration indicates the concentration in the sample solution.
References
- Rungaroon Waditee-Sirisattha, Hakuto Kageyama.
Protective effects of mycosporine-like amino acid-containing emulsions on UV-treated mouse ear tissue from the viewpoints of antioxidation and antiglycation, Journal of Photochemistry & Photobiology, B: Biology , 223 (2021) 112296
| Catalog Number | Product Name | Size |
| CSR-AAS-AGE-K05 | Elastin Anti-Glycation Assay Kit (Glyceraldehyde) | 1 KIT [96well x2] |
