Fluorescent immunostaining of exosomes produced by cancer cells using CD63 antibody (clone: 8A12)
User report
 |
Nobuyoshi Kosaka Department of Molecular and Cellular Therapy, National Cancer Center Research Institute |
Products
Manufacturer: Cosmo Bio Co., Ltd.

■ Monoclonal antibody for exosome isolation Anti CD9, CD63, CD81
This product is an antibody that specifically recognizes CD9, CD63, and CD81 known as exosome markers, and is an antibody that can isolate exosomes from serum and culture supernatant using immunoprecipitation method.
- Recognize exosome membrane proteins CD9, CD63, CD81 with high specificity
- Exosome surface antigen protein, endogenous RNA (miRNA), useful for protein analysis
Experiment content
Exosomes, which are vesicles with a diameter of about 100 nm, are vesicular granules with a lipid bilayer that are secreted extracellularly. The International Society for Extracellular Vesicles (ISEV) recommends the use of extracellular vesicle granules as a term to summarize the various secretory granules. Among the diverse secretory granules, exosomes have been defined as derived from endosomes.
The recent prosperity of exosome research has revealed the role of exosomes in many diseases. However, in order to 1) understand the physiological role of exosomes and 2) to realize disease treatment targeting exosomes, it is necessary to understand the production mechanism of exosomes. In particular, elucidation of the exosome production mechanism in cancer cells, which secrete more exosomes than other cells, may lead to new cancer treatments. Therefore, in order to understand the exosome production mechanism, we performed immunostaining for CD63, a well-known exosome marker protein, and tracked the dynamics of intracellular exosome production. Although various antibodies against human CD63 are available, an anti-human CD63 antibody (clone 8A12) marketed by Cosmo Bio was used this time.
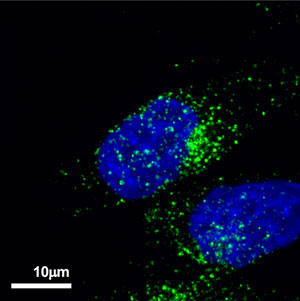
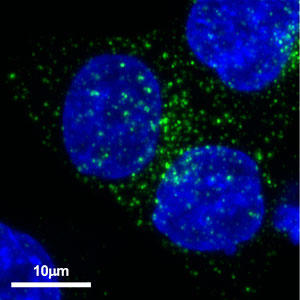
As a result, many CD63-positive granule-like structures were observed in prostate cancer cell line PC-3M (Fig. 1) and colon cancer cell line HCT116 (Fig. 2). In this experiment, staining was only with anti-human CD63 antibody, and it was only found that cancer cells had many CD63-positive granules. In the future, we would like to elucidate what genes control the production of exosomes in cancer cells by co-staining this anti-human CD63 antibody with other endosome markers.
 |
 |
| Figure 1. Localization of CD63 in prostate cancer cell PC-3M. Alexa Fluor® 488-conjugated anti-mouse secondary antibody was used as the secondary antibody. |
Figure 2. Localization of CD63 in colon cancer cells HCT116 Using Alexa Fluor® 488-labeled anti-mouse secondary antibody as secondary antibody. |
This antibody has extremely high specificity for human CD63, and administration of this antibody has succeeded in suppressing cancer metastasis caused by exosomes. It can also be used for Western blotting, immunoelectron microscopy, and ELISA. This time, it was found that it can also be used for immunostaining, so it can be said that it is an anti-human CD63 antibody with extremely high versatility in exosome research.
