- CAC Antibody Collection Index Page
Antibody Group
Advanced glycation end products (AGEs)
Autophagy and apoptosis
Bacteria-related
Calcium-binding proteins
Cancer
CD44 for enriching cancer stem cells
Tumor markers
Tumor inhibitors
Chaperones
Cytoskeleton
DNA damage
UV-induced DNA lesions
8-Nitroguanosine for oxidative stress research
Nucleotide excision repair factors
Epigenetics and chromatin
Histone H3 variants
Post-translationally-modified histone H3
Chromatin structure modifiers
Drosophila chromatin
Epitope tags
Exosomes
Extracellular matrix
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs)
Proteoglycans
Matrix and basement membrane
Cell adhesion and hemidesmosome-related
Bone and cartilage-related
Wound repair-related
Hedgehog pathway
Hormones
Immunology
Fish CD4 and CD8α
Allergic disease-related
Adaptive and innate immunity
Macrophages
Inflammatory cytokines
Viral recognition pathways
Vpr for HIV research
Insulin-like growth factor-related
Mitochondria-related
Neurobiology
Neurodegenerative disease markers
Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors
Miscellaneous
Nuclear import and export
Oxidative stress
Plant-related
Plant hormones
Plant autophagy and apoptosis
Plant stress response
Plant stress response
Proteasomes
Puromycin-specific
Reproductive biology
Small molecules
Stem cells
Novel iPS/ES markers
Pluripotency-associated
Sumoylation pathway
TGF-beta pathway
TGF-beta LAP-d
TGF-beta signaling
Transcription factors
Transporters
Tyrosine phosphatases
Ubiquitin-Proteasome Related
 CAC Antibody Collection
CAC Antibody Collection
The antibodies on this page are part of Cosmo Bio's exclusive CAC Collection. For many many thousands of other antibodies from many different makers, use our Search the Store function and our Explore Products drop down menu.
Transcription Factors
Transcription factors (TFs) directly interpret the genome, performing the first step in decoding the DNA sequence. Many function as ‘‘master regulators’’ and ‘‘selector genes’’, exerting control over processes that specify cell types and developmental patterning (Lee and Young, 2013) and controlling specific pathways such as immune responses (Singh et al., 2014). In the laboratory, TFs can drive cell differentiation (Fong and Tapscott, 2013) and even de-differentiation and trans-differentiation (Takahashi and Yamanaka, 2016). Mutations in TFs and TF-binding sites underlie many human diseases. Their protein sequences, regulatory regions, and physiological roles are often deeply conserved among metazoans (Bejerano et al., 2004; Carroll, 2008), suggesting that global gene regulatory ‘‘networks’’ may be similarly conserved. And yet, there is high turnover in individual regulatory sequences (Weirauch and Hughes, 2010), and over longer timescales, TFs duplicate and diverge. The same TF can regulate different genes in different cell types (e.g., ESR1 in breast and endometrial cell lines [Gertz et al., 2012]), indicating that regulatory networks are dynamic even within the same organism. Determining how TFs are assembled in different ways to recognize binding sites and control transcription is daunting yet paramount to under-standing their physiological roles, decoding specific functional properties of genomes, and mapping how highly specific expression programs are orchestrated in complex organisms. [from: Lambert SA, Jolma A, Campitelli LF, Das PK, Yin Y. (2018) The Human Transcription Factors. Cell. 172:650-665.]| Product name (click for order info) | Cat No (click for datasheet) |
Host | Species specificity |
| Anti Myoblast Determination Protein 1 (MYOD1/MYOD) mAb (Clone 5F11) | CAC-CE-006 | RT | MS |
| Anti CCAAT/Enhancer-Binding Protein Beta (C/EBP Beta) mAb (Clone 7D2) | CAC-CE-033 | RT | MS |
| Anti Apoptosis-Antagonizing Transcription Factor (AATF) mAb (Clone 1B2D8) | CAC-CE-034 | RT | HU MS RT |
| Anti POU Domain, Class 5, Transcription Factor 1 (POU5F1/Oct4) mAb (Clone 1C10) | CAC-CE-053 | RT | MS |
| Anti Drosophila Forkhead Box Protein O (dFOXO) pAb (Rabbit, Antiserum) | CAC-THU-A-DFOXO | RAB | Drosophila |
| Product name | Anti Myoblast Determination Protein 1 (MYOD1/MYOD) mAb (Clone 5F11) |
| Cat No | CAC-CE-011A |
| Description | MyoD is a transcription factor that induces transcription by binding with gene regulatory factors expressed in skeletal muscle. As a master regulatory gene, MyoD also determines skeletal muscle differentiation. References: 1) Harada et al. (2010) Hybridoma. 29:255-258. This antibody is used in ref.1. |
| Host | RT |
| Species specificity | MS |
| Figure 1 | 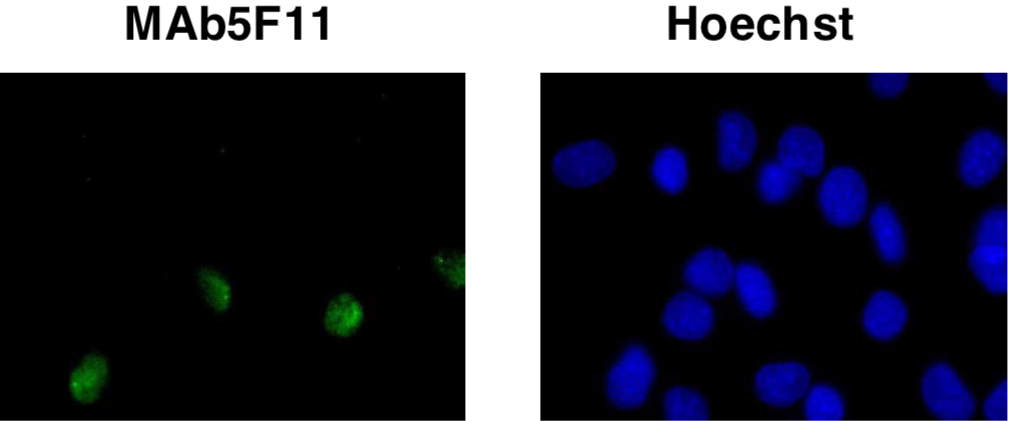 |
| Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence analysis of MyoD antibody (5F11) on C2C12 (mouse) cells. | |
| Figure 2 | 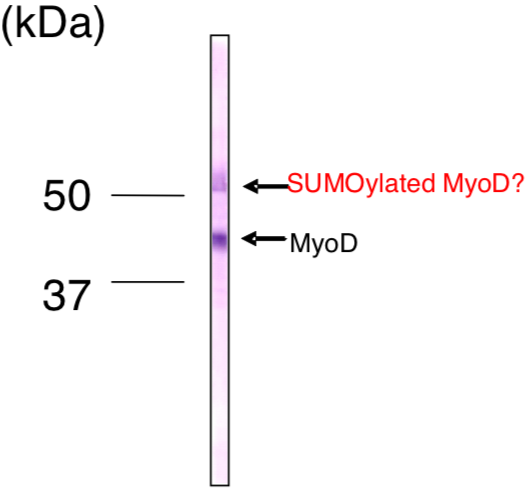 |
| Immunoblot analysis of MyoD antibody (5F11) on C2C12 cell extracts. | |
| Product name | Anti CCAAT/Enhancer-Binding Protein Beta (C/EBP Beta) mAb (Clone 7D2) |
| Cat No | CAC-CE-012A |
| Description | C/EBP β is a bZIP transcription factor which can bind as a homodimer to certain DNA regulatory regions. It can also form heterodimers with the related proteins CEBP-alpha, CEBP-delta, and CEBP-gamma. This protein is important in the regulation of genes involved in immune and inflammatory responses and has been shown to bind to the IL-1 response element in the IL-6 gene, as well as to regulatory regions of several acute-phase and cytokine genes. References: 1) Tsukada et al. (2011) Cytokine. 54:6-19. |
| Host | RT |
| Species specificity | MS |
| Figure 1 | 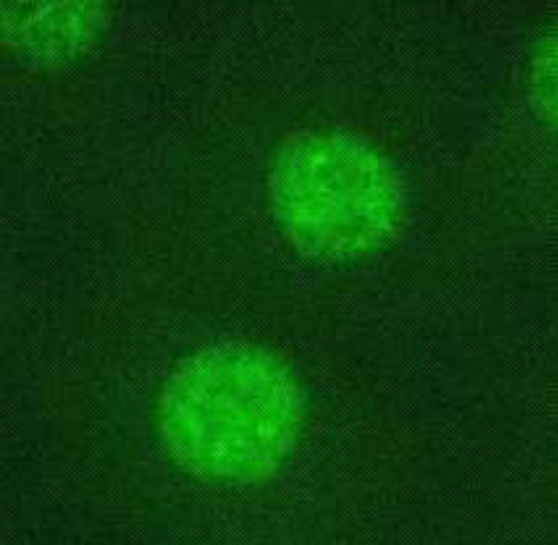 |
| Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence analysis of C/EBP beta antibody (7D2) on L929 (mouse) cells. | |
| Figure 2 | 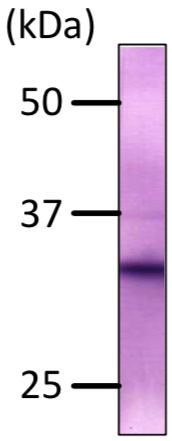 |
| Immunoblot analysis of C/EBP beta antibody (7D2) on L929 (mouse) cells total extracts. | |
| Product name | Anti Apoptosis-Antagonizing Transcription Factor (AATF) mAb (Clone 1B2D8) |
| Cat No | CAC-CE-013A |
| Description | AATF/Che-1/Traube was identified on the basis of its interaction with MAP3K12/DLK, a protein kinase known to be involved in the induction of cell apoptosis. This protein contains an extremely acidic domain and a putative leucine zipper characteristic of transcription factors. References: 1) Ishigaki et al. (2010) Cell Death Differ. 17:774-786. |
| Host | RT |
| Species specificity | HU MS RT |
| Figure 1 | 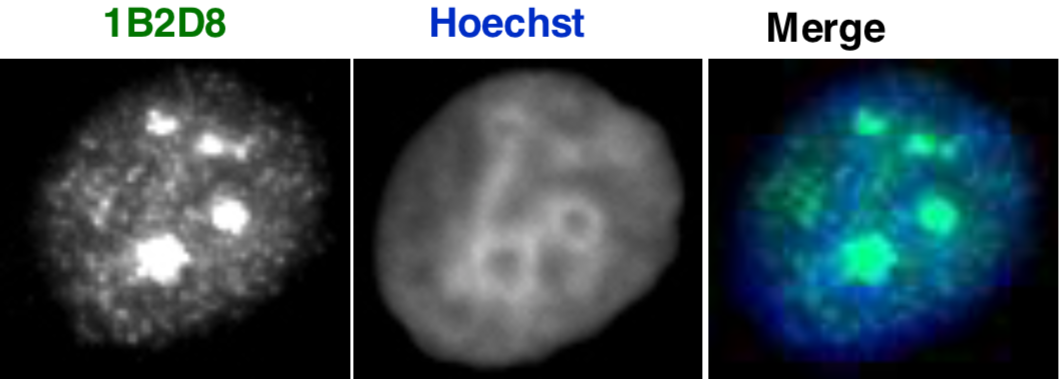 |
| Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence analysis of AATF/Che-1/Traube antibody (1B2D8) on NIH3T3 (mouse) cells. | |
| Figure 2 | 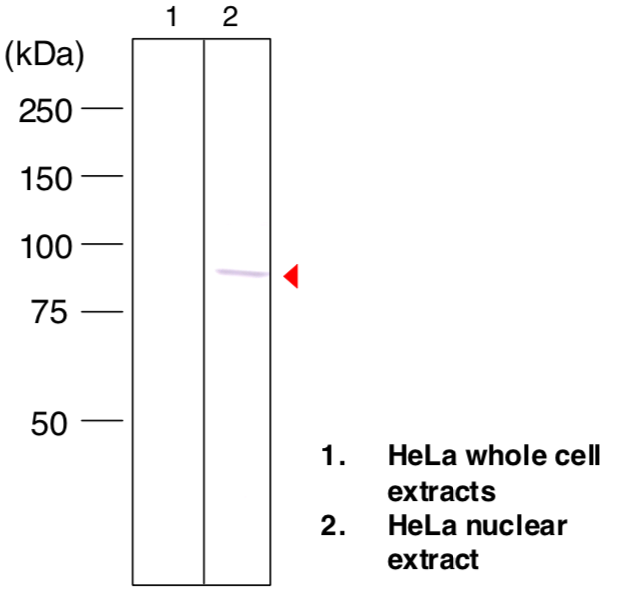 |
| Immunoblot analysis of AATF/Che-1/Traube antibody (1B2D8) on HeLa cell total and nuclear extracts. | |
| Product name | Anti POU Domain, Class 5, Transcription Factor 1 (POU5F1/Oct4) mAb (Clone 1C10) |
| Cat No | CAC-CE-052A |
| Description | Oct4/Pou5f1 is a member of POU transcription factor family, which possess POU domain. This transcription factor forms a trimeric complex with SOX2 on DNA and controls the expression of a number of genes involved in embryonic development such as YES1, FGF4, UTF1 and ZFP206. Oct4/Pou5f1 is critical for early embryogenesis and for embryonic stem cell pluripotency. References: 1) Sterneckert, J. et al. (2012) Oct4 and More: The Reprogramming Expressway. Stem Cells. 30(1):15-21. |
| Host | RT |
| Species specificity | MS |
| Figure 1 | 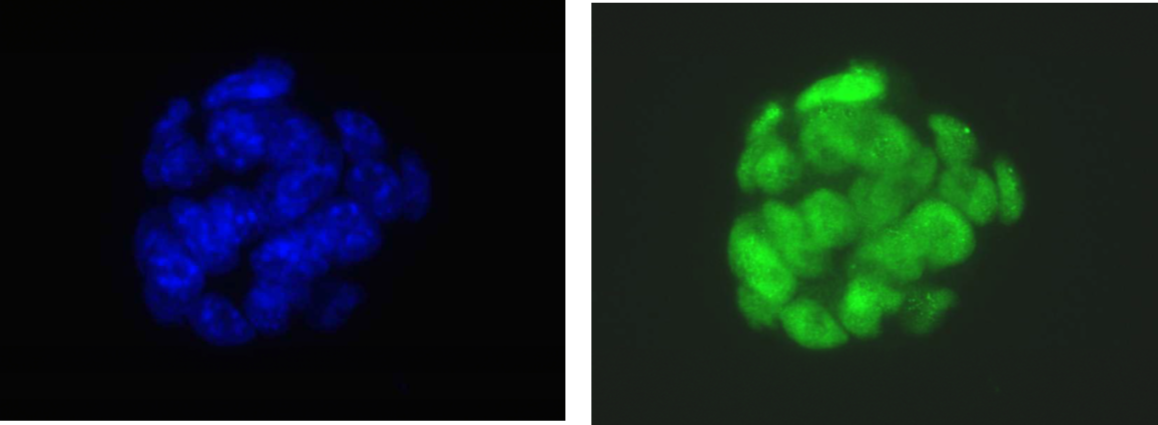 |
| Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence analysis of Oct4/Pou5f1 antibody (1C10) on mouse ES cells. DAPI (blue), Oct4 (green) | |
| Figure 2 | |
| Immunoblot analysis of Oct4/Pou5f1 antibody (1C10) on mouse ES total extracts. | |
| Product name | Anti Drosophila Forkhead Box Protein O (dFOXO) pAb (Rabbit, Antiserum) |
| Cat No | CAC-THU-A-DFOXO |
| Description | Forkhead transcription factor FoxO controls various cellular processes involved in cell cycle, cell death, metabolism and oxidative stress. Recent studies have also suggested FoxO is a key molecule for lifespan regulation of various organisms. Drosophila has a single FoxO gene (dFoxO), inactivation of which is dispensable for survival. However, dFoxO appears to regulate resistance to oxidative stress and aging in Drosophila. The activity of dFoxO is regulated by phosphorylation, ubiquitination and acetylation, which may cause multiple bands of dFoxO in western blotting using this antibody. This antibody detects endogenous levels of total dFoxO protein. References: Kanao T, et al. (2010) Activation of FoxO by LRRK2 induces expression of proapoptotic proteins and alters survival of postmitotic dopaminergic neuron in Drosophila. Hum Mol Genet. 19:3747-3758. |
| Host | RAB |
| Species specificity | Drosophila |
| Figure 1 | 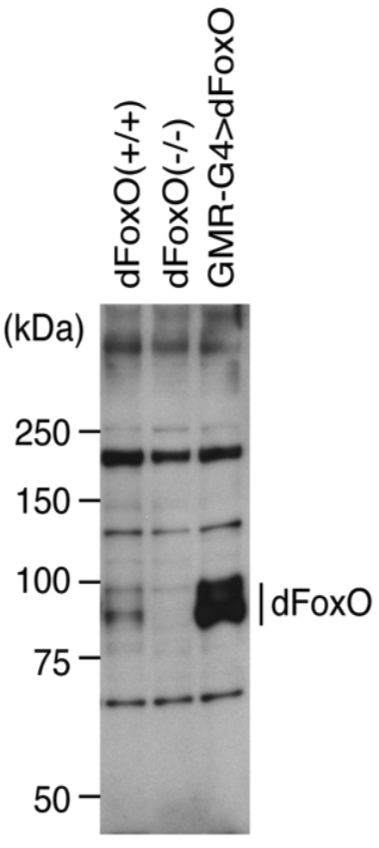 |
| Immunoblot analysis of dFoxO in the fly brain. Lysates were stained with anti-dFoxO antibody (1:3000 dilution) and detected with ECL Plus reagent. | |
| Figure 2 | 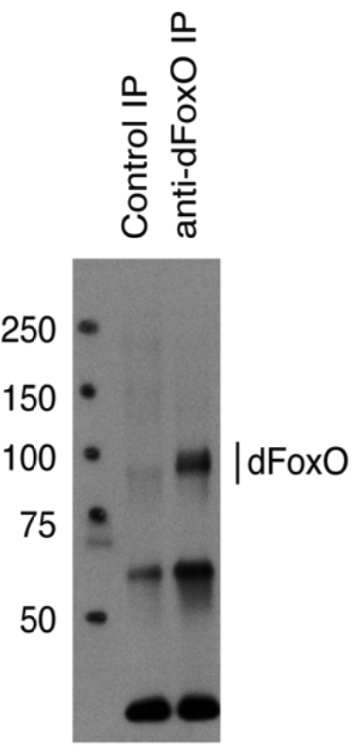 |
| IP-Western analysis of endogenous dFoxO in S2 cells. dFoxO was immunoprecipitated with anti-dFoxO antibody. | |
