- CAC Antibody Collection Index Page
Antibody Group
Advanced glycation end products (AGEs)
Autophagy and apoptosis
Bacteria-related
Calcium-binding proteins
Cancer
CD44 for enriching cancer stem cells
Tumor markers
Tumor inhibitors
Chaperones
Cytoskeleton
DNA damage
UV-induced DNA lesions
8-Nitroguanosine for oxidative stress research
Nucleotide excision repair factors
Epigenetics and chromatin
Histone H3 variants
Post-translationally-modified histone H3
Chromatin structure modifiers
Drosophila chromatin
Epitope tags
Exosomes
Extracellular matrix
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs)
Proteoglycans
Matrix and basement membrane
Cell adhesion and hemidesmosome-related
Bone and cartilage-related
Wound repair-related
Hedgehog pathway
Hormones
Immunology
Fish CD4 and CD8α
Allergic disease-related
Adaptive and innate immunity
Macrophages
Inflammatory cytokines
Viral recognition pathways
Vpr for HIV research
Insulin-like growth factor-related
Mitochondria-related
Neurobiology
Neurodegenerative disease markers
Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors
Miscellaneous
Nuclear import and export
Oxidative stress
Plant-related
Plant hormones
Plant autophagy and apoptosis
Plant stress response
Plant stress response
Proteasomes
Puromycin-specific
Reproductive biology
Small molecules
Stem cells
Novel iPS/ES markers
Pluripotency-associated
Sumoylation pathway
TGF-beta pathway
TGF-beta LAP-d
TGF-beta signaling
Transcription factors
Transporters
Tyrosine phosphatases
Ubiquitin-Proteasome Related
 CAC Antibody Collection
CAC Antibody Collection
The antibodies on this page are part of Cosmo Bio's exclusive CAC Collection. For many many thousands of other antibodies from many different makers, use our Search the Store function and our Explore Products drop down menu.
Autophagy and Apoptosis
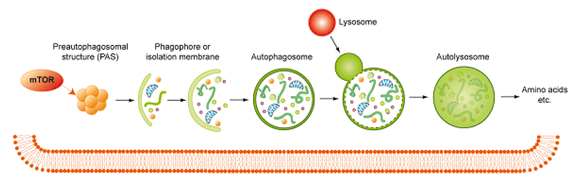
Figure 1. Formation and function of autophagosomes
In multicellular organisms, cell death is a critical and active process that maintains tissue homeostasis and eliminates potentially harmful cells. There are three major types of morphologically distinct cell death: apoptosis (type I cell death), autophagic cell death (type II), and necrosis (type III). All three can be executed through distinct, and sometimes overlapping, signaling pathways that are engaged in response to specific stimuli. Apoptosis is triggered when cell-surface death receptors such as Fas are bound by their ligands (the extrinsic pathway) or when Bcl2-family proapoptotic proteins cause the permeabilization of the mitochondrial outer membrane (the intrinsic pathway). Both pathways converge on the activation of the caspase protease family, which is ultimately responsible for the dismantling of the cell. Autophagy defines a catabolic process in which parts of the cytosol and specific organelles are engulfed by a double-membrane structure, known as the autophagosome, and eventually degraded. Autophagy is mostly a survival mechanism; nevertheless, there are a few examples of autophagic cell death in which components of the autophagic signaling pathway actively promote cell death. Necrotic cell death is characterized by the rapid loss of plasma membrane integrity. This form of cell death can result from active signaling pathways, the best characterized of which is dependent on the activity of the protein kinase RIP3. [from Green DR and Llambi F. Cell Death Signaling (2015) Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology 7(12): 1-24]
| Product name (click for order info) | Cat No (click for datasheet) |
Host | Species specificity |
| Anti Microtubule-Associated Proteins 1A/1B Light Chain 3A (MAP1LC3A/LC3) mAb (Clone LC3-1703) | CAC-CTB-LC3-2-IC | MS | HU MS |
| Anti Microtubule-Associated Proteins 1A/1B Light Chain 3A (MAP1LC3A/LC3) mAb (Clone LC3.No.6) | CAC-CTB-LC3-1-50 | MS | HU MS |
| Anti Ubiquitin-Like Modifier-Activating Enzyme ATG7 mAb (Clone ATG7-2) | CAC-CTB-AT7-M01 | MS | HU |
| Anti WD Repeat Domain Phosphoinositide-Interacting Protein 3 (WIPI-3/WDR45L) pAb (Mouse, Antiserum) | CAC-ICA-TG3-MSP1 | MS | MS |
| Anti Autophagy-Related Protein 8i (ATG8i) pAb (Rabbit, Antiserum) | CAC-KYU-TY-P01 | RAB | Soybean Arabidopsis |
| Product name | Anti Microtubule-Associated Proteins 1A/1B Light Chain 3A (MAP1LC3A/LC3) mAb (Clone LC3-1703) |
| Cat No | CAC-CTB-LC3-2-IC |
| Description | LC3 is a mammalian autophagosome marker. It is immediately cleaved to form LC3-I by Atg4, and when autophagy is induced, phosphatidylethanolamine is covalently linked to LC3-I C-terminal glycine to form LC3-II. LC3-II is membrane-bound and thought to be present in autophagosomal membranes. Since autophagosomes are degraded by fusion with lysosomes, LC3-II itself is also degraded by autophagy. Therefore, it is generally accepted that the amount of LC3-II correlates well with the amount of autophagosomes. This antibody shows good results in ICC and Immunoelectron microscopy experiments. Source: Professor Noboru Mizushima, Department of Cell Physiology, Tokyo Medical and Dental University. References: 1) Kabeya, Y., Mizushima, N., Ueno, T., Yamamoto, A., Kirisako, T., Noda, T., Kominami, E., Ohsumi, Y. and Yoshimori, T. LC3, a mammalian homologue of yeast Apg8p, is localized in autophagosome membranes after processing EMBO J. 19, 5720-5728. (2000) 2) Mizushima, N., Yoshimori, T. How to interpret LC3 immunoblotting Autophagy 3:542-545 (2007) 3) Mizushima, N., Yoshimori, T. and Levine, B. Methods in mammalian autophagy research. Cell 140; 313-326 (2010) |
| Host | Mouse |
| Species specificity | HU MS |
| Figure 1 | 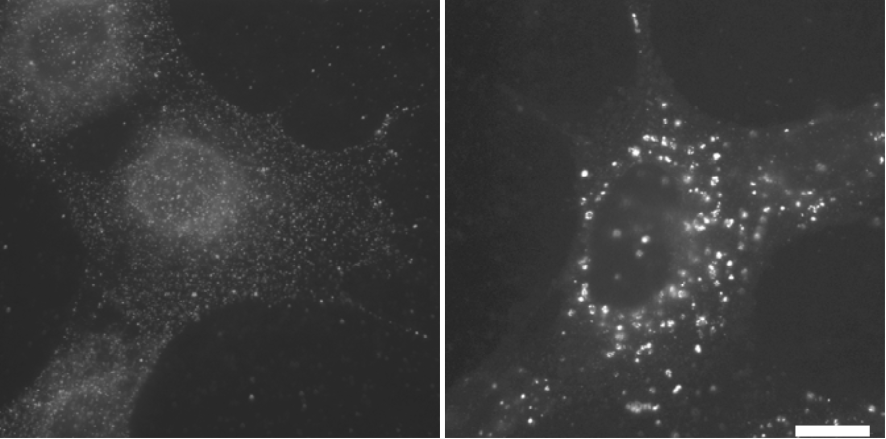 |
| Immunofluorescence microscopy analysis of mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs). MEFs were cultured in DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS (left) or DMEM without amino acids (right) for 1 hr. After fixation with 4% paraformaldehyde for 10 min at room temperature, they were permeabilized with 50μg/ml digitonin for 5 min. Cells were then subjected to immunofluorescence microscopy using #1703 anti-LC3 antibody at 1:100 dilution. Scale bar, 20μm. |
|
| Figure 2 | 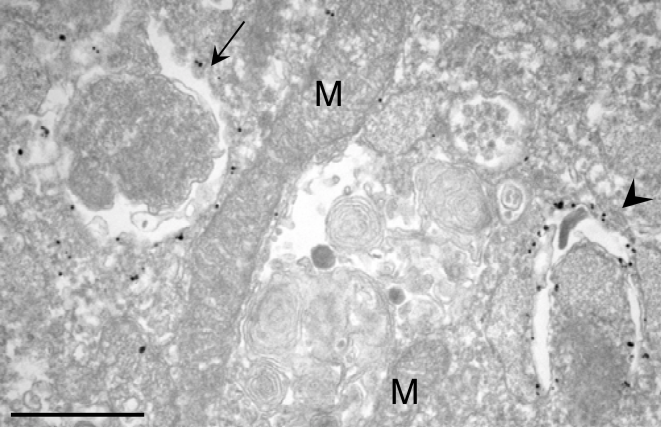 |
| Immuno-electron microscopy analysis of mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs). MEFs were cultured in DMEM without amino acids for 2 hr. After fixation with 4% paraformaldehyde for 2 hr at room temperature, they were permeabilized with liquid nitrogen. Immuno-electron microscopy analysis (pre-embedding method) of endogenous LC3 was performed using #1703 anti-LC3 antibody at 1:10 dilution. The gold labeling was intensified by using a silver enhancement kit (HQ silver enhancement kit, Nanoprobes, NY). |
|
| Product name | Anti Microtubule-Associated Proteins 1A/1B Light Chain 3A (MAP1LC3A/LC3) mAb (Clone LC3.No.6) |
| Cat No | CAC-CTB-LC3-1-50 |
| Description | LC3, a mammalian homolog of yeast Atg8, is used as a marker for autophagic vesicles (autophagosomes) formed in the process of autophagy. Immediately after synthesis, LC3 is cleaved by Atg4 to form LC3-I. When autophagy is induced phosphatidylethanolamine is covalently linked to the C-terminal glycine of LC3-I to form membrane-bound LC3-II. Most LC3-II is thought to be present in autophagosomal membranes. Since autophagosomes are degraded by fusion with lysosomes, LC3-II itself is also degraded by autophagy. Therefore, it is generally accepted that the amount of LC3-II correlates well with the amount of autophagosomes. This antibody reacts with both LC3 isoforms (LC3-I and LC3-II) and shows good results in Western blot experiments. References: 1) Kabeya, Y., Mizushima, N., Ueno, T., Yamamoto, A., Kirisako, T., Noda, T., Kominami, E., Ohsumi, Y. and Yoshimori, T. LC3, a mammalian homologue of yeast Apg8p, is localized in autophagosome membranes after processing EMBO J. 19, 5720-5728. (2000). 2) Mizushima, N., Yoshimori, T. How to interpret LC3 immunoblotting Autophagy 3:542-545 (2007). |
| Host | Mouse |
| Species specificity | HU MS |
| Figure 1 | 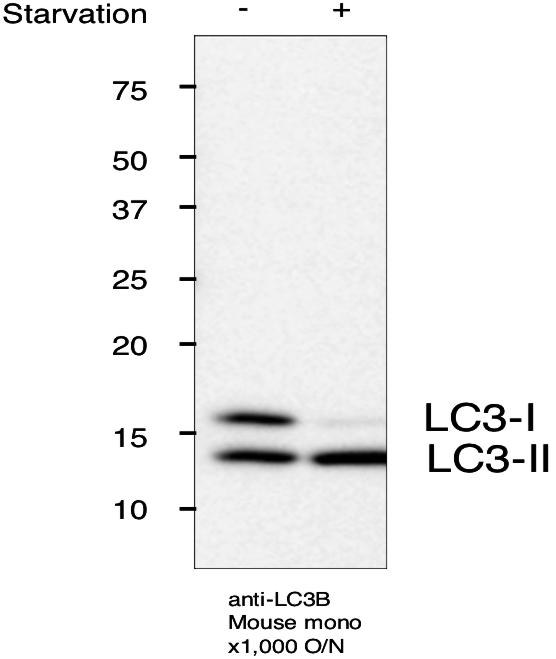 |
| Immunoblot for LC3B. MEFs +/- starvation for 2 hr SDS-PAGE (MEF lysate 15 ug/lane, 15% gel) Transfer to PVDF membrane (semi-dry blotter, 100 mA/gel 1hr) Expose ECL 5min |
|
| Product name | Anti Ubiquitin-Like Modifier-Activating Enzyme ATG7 mAb (Clone ATG7-2) |
| Cat No | CAC-CTB-AT7-M01 |
| Description | Autophagy is an evolutionarily conserved process, in which autophagosomes fuse with lysosomes and degrade bulk cytoplasmic contents. Autophagy is involved in many physiological processes, including development, infection, cancer, and neurodegenerative diseases. ATG (autophagy-related) genes were identified by genetic screening in yeast. Atg7 acts as an E1-like enzyme in both Atg12 and Atg8 ubiquitin-like conjugation systems. Atg7 transfers Atg12 to an E2-like enzyme Atg10, and conjugates Atg12 to Atg5. Atg7 also transfers Atg8 to another E2-like enzyme Atg3, and conjugates Atg8 to phosphatidylethanolamine. Many of these ATG genes are conserved in mammals. Atg7 deficient neonates die soon after birth from perineonatal starvation. Conditional deletion of Atg7 in the nervous system results in neurodegeneration with ubiquitin containing aggregates. Source: Dr. Shigeomi Shimizu, Pathology and Cell Biology, Research Institute for Intractable Diseases, Tokyo Medical and Dental University. References: 1) Klionsky and Emr, 2000, Science, 290, 1717-21. 2) Mizushima et al., 2008, Nature, 451, 1069-75. 3) Tsukada and Ohsumi, 1993, FEBS Lett, 333, 169-74. 4) Mizushima et al., 1998, Nature, 395, 395-8. 5) Komatsu et al., 2005, J Cell Biol, 169, 425-34. 6) Komatsu et al., 2006, Nature, 441, 880-4. |
| Host | Mouse |
| Species specificity | HU |
| Figure 1 | 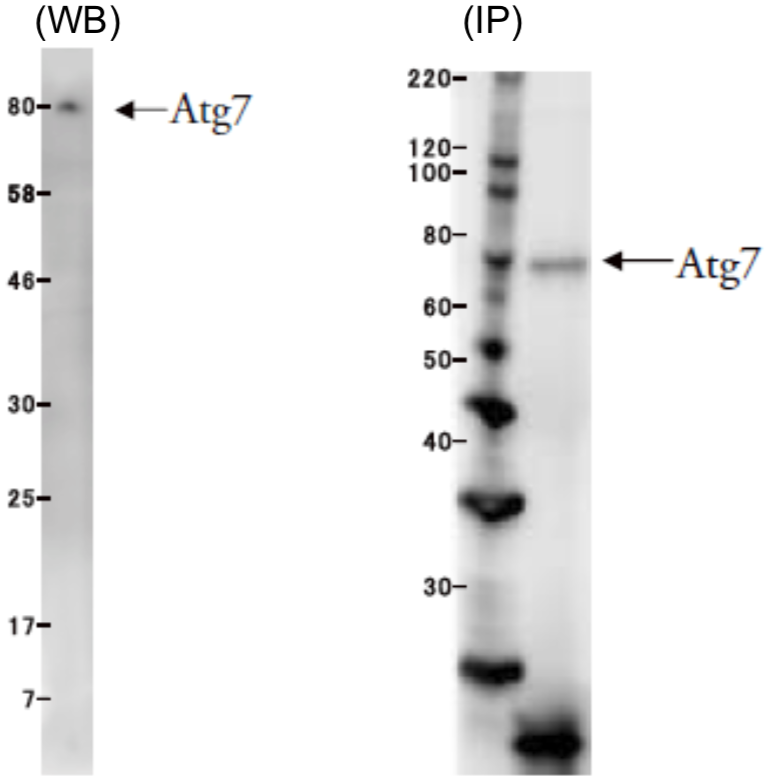 |
| Left: Western blot application example using HeLa cell extract Right: IP application example using HeLa cell extract |
|
| Product name | Anti WD Repeat Domain Phosphoinositide-Interacting Protein 3 (WIPI-3/WDR45L) pAb (Mouse, Antiserum) |
| Cat No | CAC-ICA-TG3-MSP1 |
| Description | WDR45L is a ubiquitously expressed WD40 repeat protein upregulated in a variety of tumor tissues including ovarian and uterine cancers. WDR45L, also known as WIPI-3, comprises seven 40 amino acid (WD40) repeats. WD40 repeats are found in many eukaryotic proteins that coordinate multi-protein complex assemblies. WD40 proteins are implicated in multiple functions, including adaptor/regulatory modules in signal transduction, pre-mRNA processing and cytoskeleton assembly. This protein regulates cell cycle transcription and signal transduction, and it is believed to be involved in cell death by apoptosis and autophagy. In recent years, it has also been used as a marker for neurodegenerative diseases associated with cell death. |
| Host | Mouse |
| Species specificity | MS |
| Figure 1 | 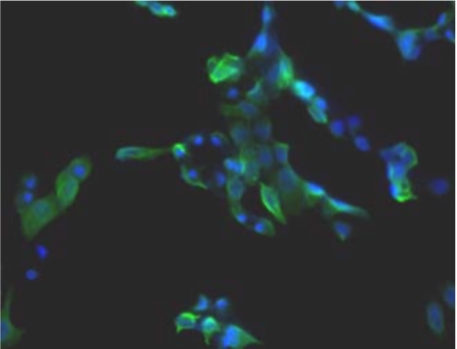 |
| Immunohistochemistry. Hela cells ICAFectin441-transfected with a plasmid encoding mouse WDR45L were fixed, permeabilized and stained with rat anti-human ITIH4 serum (diluted 1/100) and Alexa488 goat anti mouse IgG secondary antibody. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. |
|
| Figure 2 | 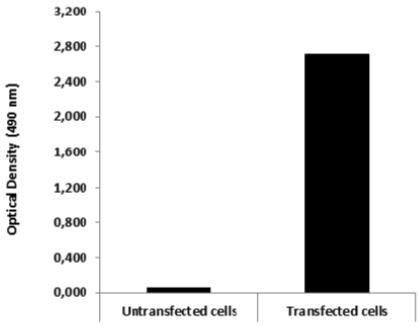 |
| ELISA. Lysates of HeLa cells untransfected and ICAFectin441-transfected with a plasmid encoding mouse WDR45L were coated in 96 wells plate. Wells were stained with mouse anti-mouse WDR45L serum and HRP goat anti rat IgG secondary antibody. |
|
| Product name | Anti Autophagy-Related Protein 8i (ATG8i) pAb (Rabbit, Antiserum) |
| Cat No | CAC-KYU-TY-P01 |
| Description | ATG8 is an autophagy related protein, homologous to LC3. ATG8 is conjugated with phosphatidylethanolamine at its C terminal glycine via ATG7 and ATG3, E1 and E2-like enzymes, respectively. Higher plants such as Arabidopsis have multiple ATG8 homologs comprising two subfamilies: ATG8a-g and ATG8h-i. Anti-soybean ATG8i antibody was raised against GST-fused GmATG8i. It cross-reacts with plant ATG8h-i but not with ATG8a-g proteins. References: 1) Htwe NMPS, Tanigawa H, Ishibashi Y, Zheng SH, Yuasa T and Iwaya-Inoue MI. (2009) Nutrient starvation differentially regulates GmATG8i in soybean seedlings. Plant Biotechnol. 26:317-326. 2) Okuda M, Htwe NMPS, Oshima K, Ishibashi Y, Zheng SH, Yuasa T and Iwaya-Inoue MI. (2011) Ethylene signal mediates induction of GmATG8i in soybean plants under starvation stress, Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 75(7):1408-12. PMID: 21737912 |
| Host | RAB |
| Species specificity | Soybean Arabidopsis Plant |
