this page: Human Collagen IVα Rat Monoclonal Antibodies Dashboard
Product and Ordering Information
Antibody Specifications
Image Gallery
References
Citations
Flyers
Human Collagen IVα Monoclonal Antibodies
Datasheets
Alport Cocktail Datasheet
Key References
Kagawa M et al.
Borza DB et al.
Sado et al.
Human Collagen IVα Rat Monoclonal Antibodies Dashboard

Powerful Tools for Collagen IV and Alport Syndrome Research
Anti-Collagen 4 Cocktail mAb (Clones H53, B51, H25)
(Cat. No SGE-CFT45325)
Alport syndrome is an inherited disease characterized by the pathological absence or reduction of the collagen α5(IV) chain in glomerular basement membrane (GBM), tubular basement membrane (TBM) and Bowman's capsular basement membrane. Anti-Collagen 4 Cocktail mAb (Clones H53, B51, H25) is a cocktail of three different rat mAbs for easy and rapid staining of human renal and skin biopsy sections to distinguish Alport syndrome from normal tissue. It comprises two different FITC-conjugated mAbs (clones H53 and B51) that reveal the α5(IV) chain in glomerular, tubular and Bowman's capsular BMs and a Texas Red-conjugated mAb (clone H25) that targets α2(IV) to reveal endothelial basement membrane structure.
 |
 |
|
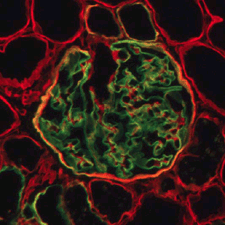
Two-color fluorescence image of a normal human kidney section stained with Anti-Collagen 4 Cocktail mAb (Clones H53, B51, H25). FITC fluorescence (α5(IV) chain) is observed in the GBM, part of the TBM and Bowman's capsular BM. BMs where both FITC and Texas Red are present appear orange to yellow. |
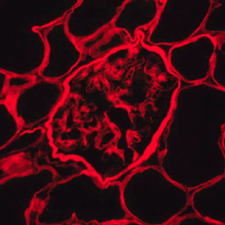
Two-color fluorescence image of an X-linked Alport syndrome kidney section stained with Anti-Collagen 4 Cocktail mAb (Clones H53, B51, H25). The absence of FITC fluorescence indicates loss of the α5(IV) chain while the maintenance of Texas Red fluorescence targeting the α2(IV) chain highlights endothelial BM structures. |
Product and Ordering Information TOP

CosmoBio USA is pleased to offer Anti-Collagen 4 Cocktail mAb (Clones H53, B51, H25) (antibody cocktail): a rapid, easy and reliable method to characterize Alport syndrome patient samples. It replaces a previous complicated, time-consuming and labor-intensive approach that required a denaturation step to reveal epitopes and that employed indirect immunofluorescence staining. Instead, the improved approach employs denaturation-free, two-color direct staining of collagen α5(IV) and α2(IV) chains with fluorochrome-conjugated, epitope-defined rat monoclonal antibodies against collagen triple-helical and NC1 domains. Also sold individually (labeled and unlabeled), these epitope-defined monoclonal antibodies are useful for research on hereditary diseases related to collagen IV. |
|||||||
| Human Collagen IVα Rat Monoclonal Antibodies | |||||||
| Anti-Collagen 4 Cocktail mAb (Clones H53, B51, H25) TOP | |||||||
| Clone (Click for datasheet) |
Label | Specificity | Size | Acid Treatment Required |
Storage | Application | Catalog Number (Click for order information) |
| H53 | FITC | α5 | 1 ml | no | 4°C dark | IF (frozen sections) | SGE-CFT45325 |
| B51 | FITC | α5 | |||||
| H25 | Texas Red | α2 | |||||
| Individual Antibodies TOP | |||||||
| Clone (Click for datasheet) |
Label | Specificity | Size | Acid Treatment Required |
Storage | Application | Catalog Number (Click for order information) |
| H53 | FITC | α5 | 0.5 ml | no | 4°C dark | IF (frozen sections) | SGE-CFT453 |
| H53 | none | α5 | 0.5 ml | no | -20°C | IF (frozen sections) | SGE-C453 |
| B51 | FITC | α5 | 0.5 ml | no | 4°C dark | IF (frozen sections) | SGE-CFT451 |
| B51 | none | α5 | 0.5 ml | no | -20°C | IF (frozen sections) | SGE-C451 |
| H25 | Texas Red | α2 | 0.5 ml | no | 4°C dark | IF (frozen sections) | SGE-CFT425 |
| H25 | none | α2 | 0.5 ml | no | -20°C | IF (frozen sections) | SGE-C425 |
| H52 | none | α5 | 0.5 ml | yes | -20°C | WB, IF (frozen sections) | SGE-C452 |
Antibody Specifications TOP
| Clone | Subclass | Specificity | α1 | α2 | α3 | α4 | α5 | α6 | Epitope |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Four different anti-human collagen IVα clones | |||||||||
| H53 | IgG2a,k | Imperfection III | - | - | - | - | + | - | IDVEF |
| B51 | IgG2a | NC1 domain | - | - | - | - | + | - | unknown |
| H25 | IgG1,k | Imperfection XIII | - | + | - | - | - | - | EAIQP |
| H52 | IgG2b,k | NCI domain | - | - | - | - | + | - | SKPQSETL |
Image Gallery TOP
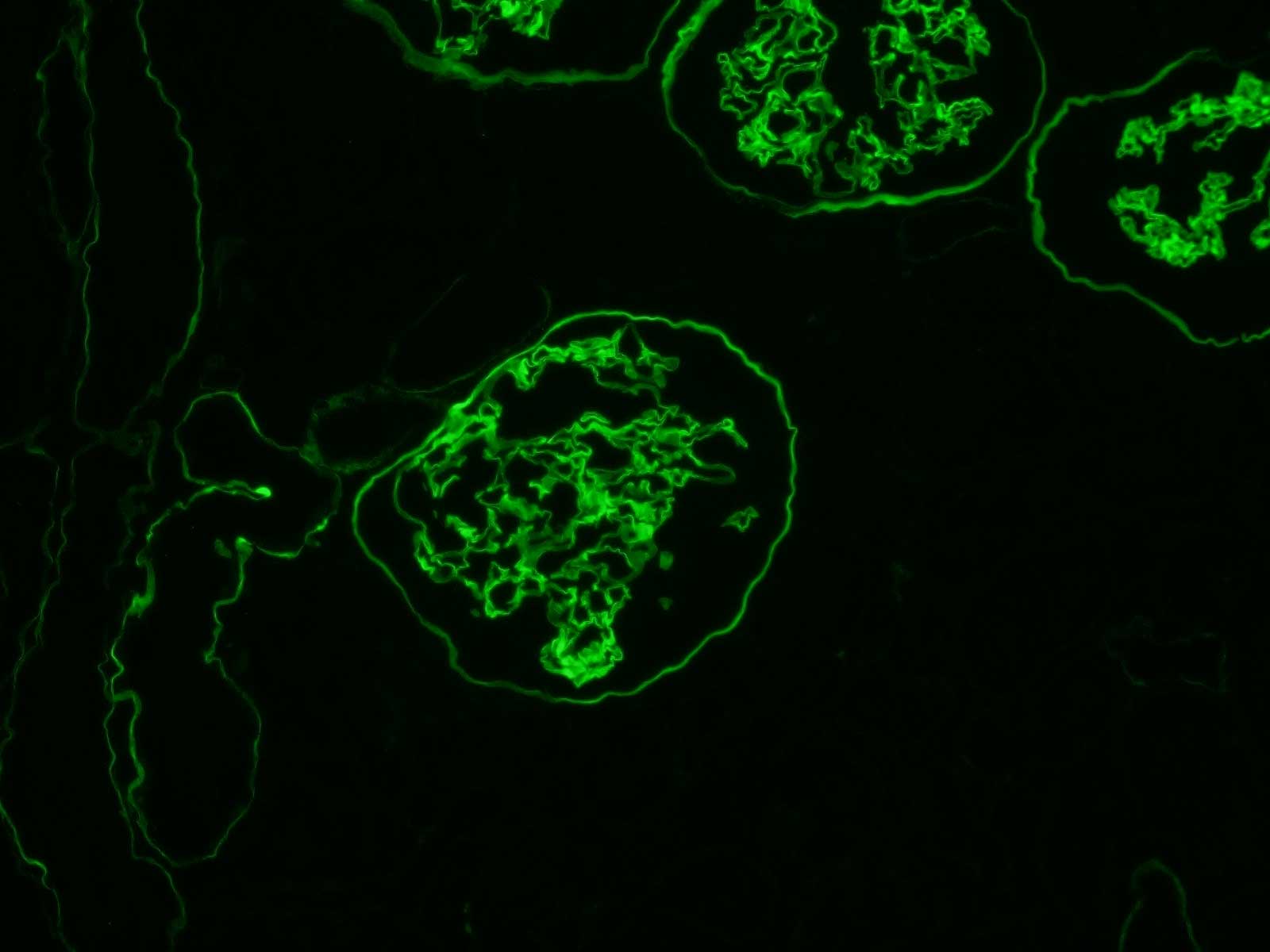
Clone H53
Human kidney cryostat section stained with monoclonal antibody H53. H53 is ideal for staining glomerular, Bowman's capsular and partial renal tubular basement membranes.
Clone B51
Human kidney cryostat section stained with monoclonal antibody B51. B51 is ideal for staining glomerular, Bowman's capsular and partial renal tubular basement membranes.

Larger image unavailable
Clone H52
Human kidney cryostat section stained with monoclonal antibody H52 reveals glomerular, partial tubular, and Bowman's capsular basement membranes.
Clone H25
Human kidney cryostat section stained with monoclonal antibody H25. H25 is ideal for staining of glomerular, Bowman's capsular, renal tubular and capillary vessel basement membranes.

Larger image unavailable
Cocktail, Normal Tissue
Two-color fluorescence image of a normal human kidney section stained with Anti-Collagen 4 Cocktail mAb (Clones H53, B51, H25). FITC fluorescence (α5(IV) chain) is observed in the GBM, part of the TBM and Bowman's capsular BM. BMs where both FITC and Texas Red are present appear orange to yellow.

Larger image unavailable
Cocktail, Alport Tissue
Two-color fluorescence image of an X-linked Alport syndrome kidney section stained with Anti-Collagen 4 Cocktail mAb (Clones H53, B51, H25). The absence of FITC fluorescence indicates loss of the α5(IV) chain while the maintenance of Texas Red fluorescence targeting the α2(IV) chain highlights BM structures.
References TOP
- Kagawa M et al. Back
Epitope-defined monoclonal antibodies against type-IV collagen for diagnosis of Alport syndrome.
Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 12: 1238-1241 (1997) (PMID: 9198058) - Borza DB et al. Back
The NCI domain of collagen IV encodes a novel network composed of the α1, α2, α5, and α6 chains in smooth muscle basement membranes.
J. Biol. Chem. 276: 28532-28540 (2001) (PMID: 11375996) - Sado et al. Back
Establishment by the rat lymph node method of epitope-defined monoclonal antibodies recognizing the six different α chains of human type IV collagen.
Histochem. Cell Biol. 104: 267-275 (1995) (PMID: 8548560) - Yoshioka K et al.
Type IV collagen α5 chain: Normal distribution and abnormalities in X-linked Alport syndrome revealed by monoclonal antibody.
Am. J. Pathol. 144: 986-996 (1994) (PMID: 8178947) - Ninomiya Y et al.
Differential expression of two basement membrane collagen genes, COL4A6 and COL4A5, demonstrated by immunofluorescence staining using peptide-specific monoclonal antibodies.
J. Cell Biol. 130: 1219-1229 (1995) (PMID: 7657706) - Naito I et al.
Relationship between COL4A5 gene mutation and distribution of type IV collagen in male X-linked Alport syndrome.
Kidney Int. 50: 304-311 (1996) (PMID: 8807602)
Citations TOP
- Bu L et al.
Somatic Mosaicism in a Male Patient With X-linked Alport Syndrome.
Kidney Int Rep. 14(4): 1031-1035 (2019) (PMID: 31312776) - Samar M et al.
Negative Staining for COL4A5 Correlates With Worse Prognosis and More Severe Ultrastructural Alterations in Males With Alport Syndrome.
Kidney Int Rep. 2(1): 44-52 (2017) (PMID: 29142939) - Malone AF et al.
Functional assessment of a novel COL4A5 splice region variant and immunostaining of plucked hair follicles as an alternative method of diagnosis in X-linked Alport syndrome.
Pediatr Nephrol. 32(6): 997-1003 (2017) (PMID: 28013382) - Nozu K et al.
X-linked Alport syndrome caused by splicing mutations in COL4A5.
Am Soc Nephrol. 9(11): 1958-64 (2014) (PMID: 25183659) - Matsubara S et al.
Pregnancy complicated with Alport syndrome: a good obstetric outcome and failure to diagnose an infant born to a mother with Alport syndrome by umbilical cord immunofluorescence staining.
Obstet Gynaecol Res. 35(6): 1109-14 (2009) (PMID: 20144175) - Patey-Mariaud de Serre N et al.
Collagen alpha5 and alpha2(IV) chain coexpression: analysis of skin biopsies of Alport patients.
Kidney Int. 72(4): 512-6 (2007) (PMID: 17554254) - Kharrat M et al.
Autosomal dominant Alport's syndrome: study of a large Tunisian family.
Kidney Dis Transpl. 17(3): 320-5 (2006) (PMID: 16970251)