Anti-glycation / Aging related
Collagen AGEs Anti-Glycation Assay Kit (Specific AGEs)
Rapid detection of CMA / CML by ELISA method | Series related to aging / glycation research
This kit is for rapid ELISA detection of CMA (carboxymethylarginine) or CML (carboxymethyllysine) produced when collagen immobilized on a plate is saccharified with glyoxal.
Substances that inhibit the glycation reaction of collagen can be easily screened.
Background
Saccharides are essential nutrients for life activities, but on the other hand, they modify the lysine and arginine residues of proteins in the body and change the charge of the protein, which changes the three-dimensional structure of the protein. known to have a significant impact on This reaction is called the Maillard reaction (glycation) or saccharification. The early reaction produces Amadori rearrangement products, and the late reaction leads to advanced glycation end-products (AGEs) through reactions such as oxidation, dehydration, and condensation. can be divided into Collagen, a structural protein that forms all organs such as skin, blood vessel walls, and bones, is no exception and undergoes glycation.
Carboxymethyllysine: Nε-(carboxymethyl) lysine: CML is a type of non-fluorescent, non-crosslinking AGEs, and glycosylated protein lysine residues (fructose lysine) generate hydroxyl radicals from transition metals (1), Nitric oxide-derived peroxynitrite (2) and hypochlorous acid (3) produced by inflammatory reactions are oxidized sugar oxidation products that are reported to be major antigenic AGE structures in living organisms (Four). CML is also known to be produced via glyoxal, which is produced from the oxidative decomposition of glucose. CML is an indicator of long-term accumulation of oxidative stress, such as accumulation in skin collagen with aging, and its association with atherosclerosis, diabetes, Alzheimer's disease, etc. has also been pointed out.
Carboxymethylarginine: Nω-(carboxymethyl)arginine: CMA is one of the AGEs produced by the reaction of glyoxal and arginine. In addition, CMA is characterized as non-fluorescent and non-crosslinking AGEs, and has been reported to be produced specifically in collagen (1). It is said that accumulation of AGEs in biological collagen adversely affects fibroblasts along with collagen denaturation, causing not only blood vessels but also skin aging.
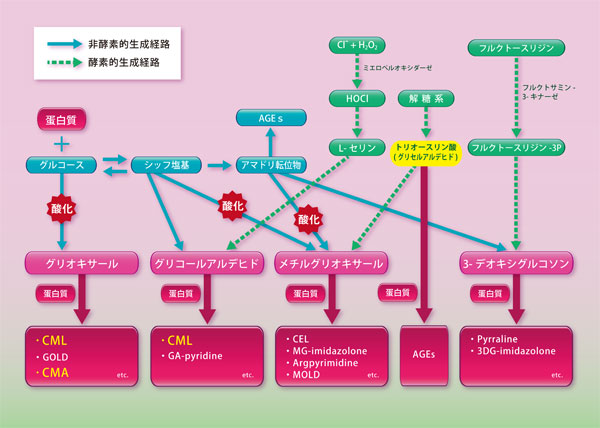
Figure 1 In vivo AGE production pathway
Features
- It is possible to easily screen substances that inhibit the glycation reaction of collagen.
- Useful for developing anti-glycation materials in the development of functional foods and cosmetics
Composition
| content | capacity | quantity |
| Collagen-immobilized 96-well plate (with aluminum pouch) | 8 wells x 12 strips | 1 sheet |
| plate seal | - | 2 sheets |
| Aminoguanidine solution (10mM) *anti-glycation standard substance | 250uL | One |
| Specimen diluent | 30 mL | One |
| glyoxal solution | 5mL | One |
| Wash buffer (x10) | 50 mL | One |
| blocking buffer | 50 mL | One |
| Antibody (anti-CMA antibody or anti-CML antibody) (x100) | 100uL | One |
| HRP-conjugated secondary antibody (x100) | 100uL | One |
| coloring liquid | 10 mL | One |
| Stop liquid | 10 mL | One |
*This kit is capable of assaying one 96-well plate.
Example
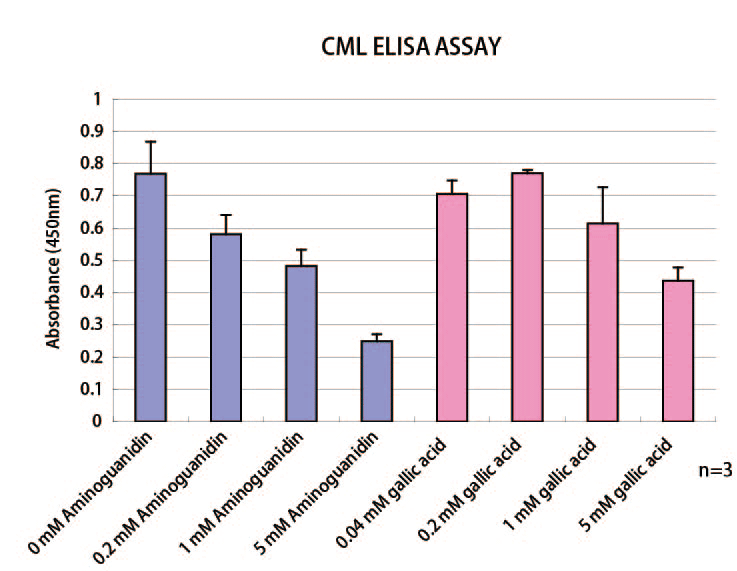
Fig. 2 Collagen AGEs anti-glycation assay kit <CML-specific, glyoxal> (Product number: AAS-AGE-K02)
Search for anti-glycation materials using CML generated from glycated collagen glycated with glyoxal for one day.
Concentrations indicate final concentrations in wells.
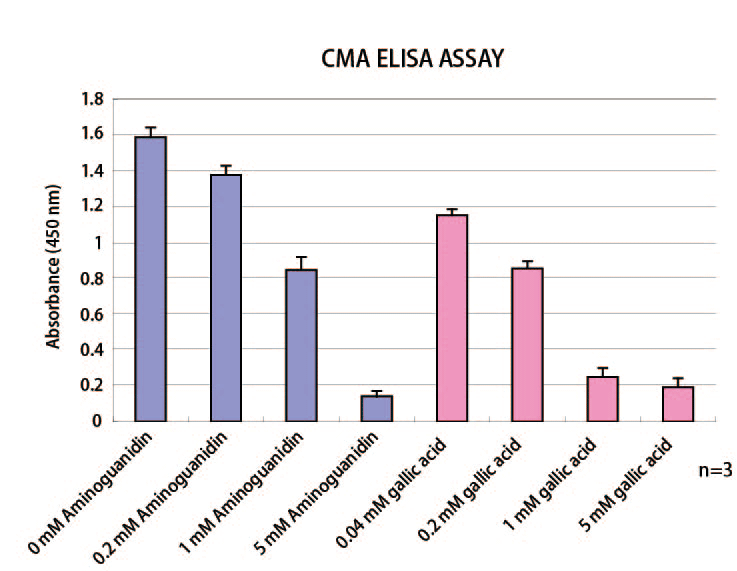
Fig. 3 Collagen AGEs anti-glycation assay kit <CMA-specific, glyoxal> (Part number: AAS-AGE-K03)
Exploring anti-glycation materials using CMA generated from glycated collagen glycated with glyoxal for 7 days.
Concentrations indicate final concentrations in wells.
| Catalog Number | Product Name | Size |
| CSR-AAS-AGE-K02 | Collagen AGEs Assay Kit, CML-Specific, Glyoxal | 1 Kit |
| CSR-AAS-AGE-K03 | Collagen AGEs Assay Kit, CMA-Specific, Glyoxal | 1 Kit |
